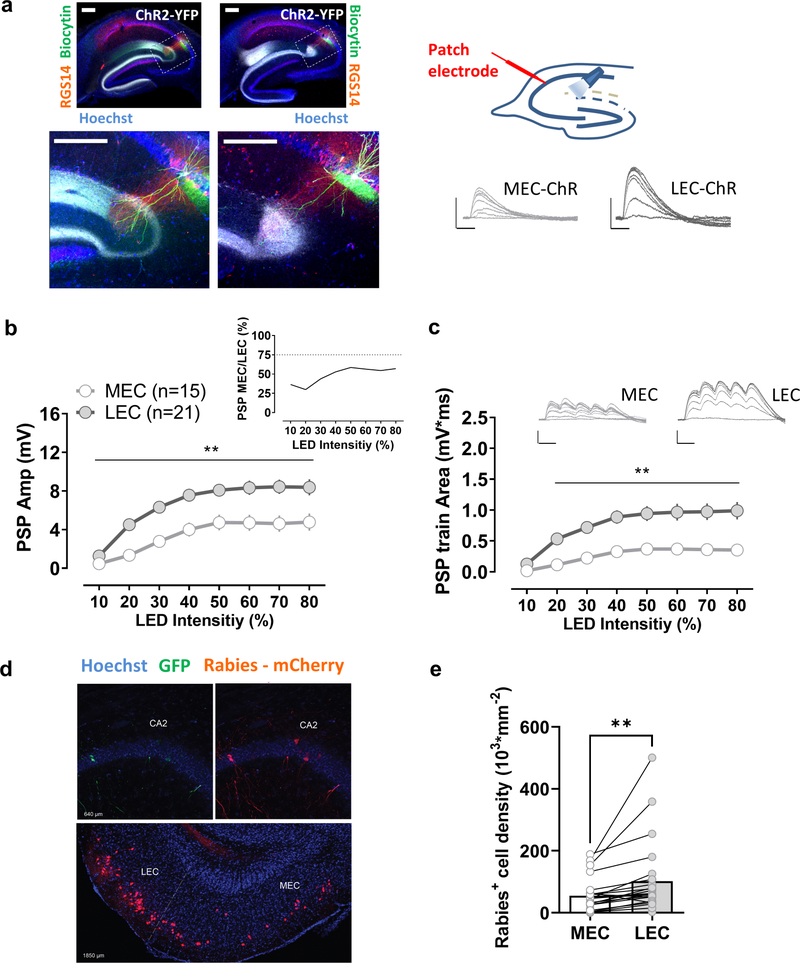
Figure 1. Comparison of synaptic responses of CA2 pyramidal neurons to their direct medial and lateral entorhinal cortical inputs.
a, An AAV was injected to express ChR2 in the medial (MEC) or the lateral entorhinal cortex (LEC). Transverse hippocampal sections show MEC or LEC ChR2-YFP-labelled fibers, as well as biocytin-filled CA2 neurons and staining for the CA2 region marker RGS14 at low (upper panels) and high magnification (lower panels). Photostimulation of ChR2-expressing terminals in the stratum lacunosum moleculare evoked a large postsynaptic potential in CA2 pyramidal neurons in acute hippocampal slices for both, MEC and LEC injected groups. The LEC-evoked response (21 cells from 21 slices from 7 animals) was significantly larger than the MEC-evoked response (15 cells from 15 slices from 5 animals) using either a single light pulse (b) or a short train of optical stimuli (c). d, Monosynaptic contacts to dorsal CA2 from the entorhinal area originate largely from the LEC. Retrograde tracing from dorsal CA2 using G-deleted rabies virus expressing mCherry (Rabies- mCherry), after CA2 infection with a Cre-dependent helper virus (expressing GFP). Coronal hippocampal sections in the upper panel and entorhinal horizontal slice in the lower panel. e, The number of mCherry positive cells is greater in LEC than MEC (23 sections from 5 animals). Scale bars: 5 mV/25 ms and 200 μm. In b and c **: p<0.01 Holm-Sidak’s post hoc test after two-way mixed-design ANOVA (in b: F=4.963 p<0.0001 for interaction Stim LED Intensity x PP M-L; in c: F=9.479, p<0.0001 for interaction Stim LED Intensity x PP M-L); in e **: p<0.01, paired t-test.