Figure 2.
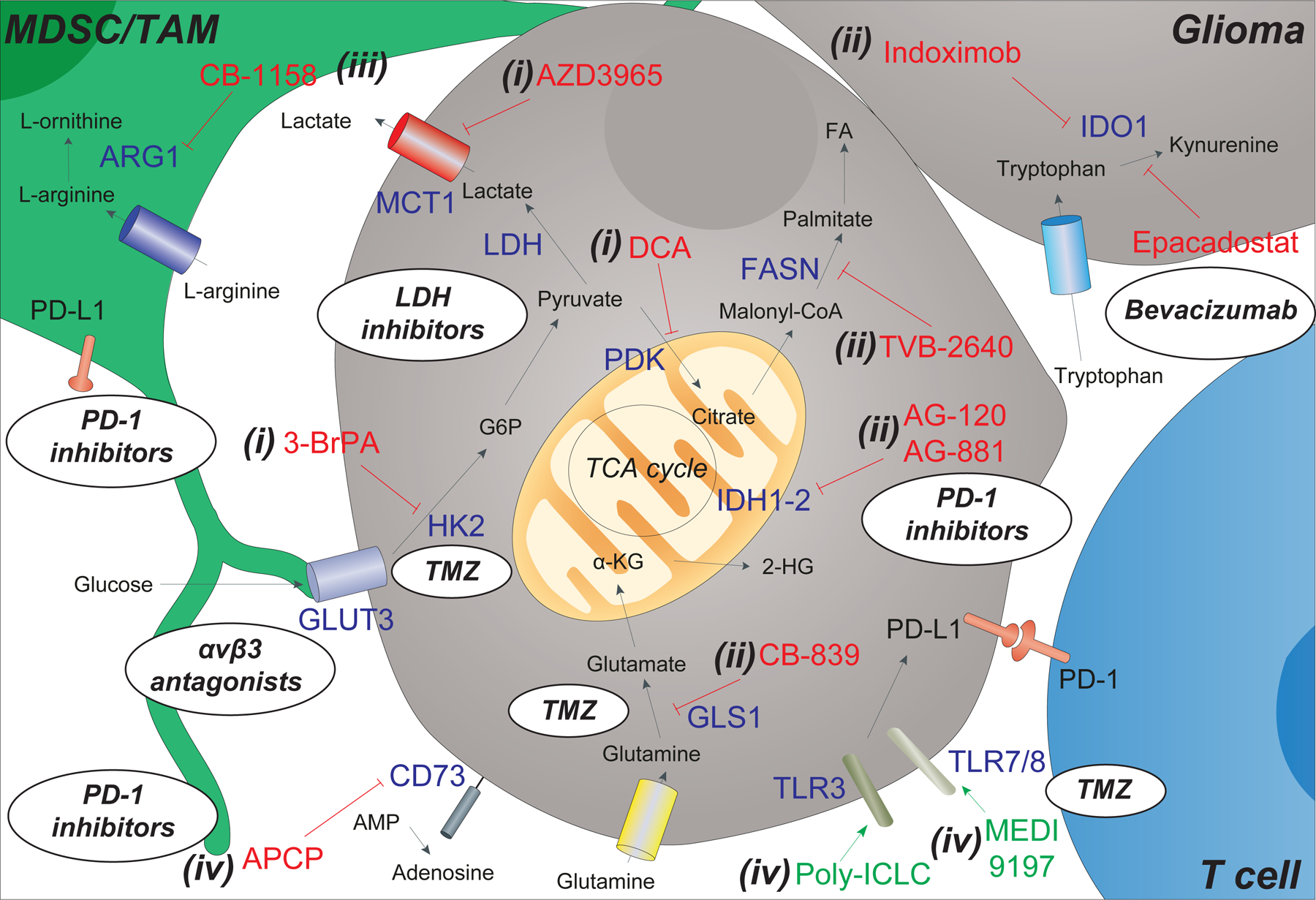
Targeting tumor metabolism in gliomas with biologics and small molecule inhibitors. Cell metabolism and the availability of metabolic substrates in the glioma microenvironment is dependent on the activity of multiple cell types, including myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), tumor associate macrophages (TAMs), glioma cells, and T cells. Inhibitors (in red) and agonists (in green) aimed at interfering with specific targets (blue) of this complex metabolic network have been developed and are under clinical testing. These include (i) inhibitors that act on altered glucose and lactate metabolism in gliomas [such as 3-brompyruvate (3-BrPA), dichloroacetate (DCA) and AZD3965]; (ii) inhibitors of other metabolic enzymes in glioma [such as isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDH) 1–2 via ivosidenib (AG-120) and vorasidenib (AG-881), glutaminase (GLS1) via CB-839, fatty acid synthase (FASN) via TVB-2640, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO)1 via indoximod (1-MT) and epacadostat (INCB024360)]; (iii) inhibitors of arginase (ARG) 1 in TAM via molecules such as CB-1158; and (iv) modulators of membrane bound proteins [such as the 5′-nucleotidase CD73 via α, β-methylene ADP (APCP), and the toll like receptors (TLRs) 3–7/8 via the agonists poly (I:C) stabilized by lysine (poly-ICLC) and MEDI9197]. Oval inserts/bubbles show how current and/or future combination of immunotherapies and chemotherapies can be used to overcome certain metabolic alterations of the glioma. These include the use of αvβ3 antagonists to target glioma cells overexpressing GLUT3, LDH inhibitors (e.g., NCI-006) to target the overexpression of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), bevacizumab (VEGF inhibitor) in combination with epacadostat (IDO inhibitor), PD-1 inhibitors that are used in synergy with APCP, AB-881, and CB-1158 treatments, and finally the combination of temozolomide (TMZ) with TLR inhibitors and HK2 inhibitors (the latter being able to significantly enhance the efficacy of TMZ treatment).
Other abbreviations: FA (fatty acids), α-KG (α -ketoglutarate), 2-HG (2-hydroxyglutarate), GSH (glutathione), adenosine monophosphate (AMP), Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1).
