Table 2.
Enzymatic kinetics of trypsin inhibition by metabolites in bilirubin deconjugation pathway
| Inhibitor Name | Structure | Kobs (s−1) | k2/Ki (M−1s−1) | IC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||
| Biliverdin |
|
0.001822 | 181.8182 | 12.68 |
| Conjugated Bilirubin |
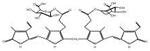
|
0.004937 | 500 | 4.679 |
| Unconjugated Bilirubin |
|
0.006642 | 666.6667 | 3.478 |
| Mesobilirubin |
|
0.005981 | 588.2353 | 3.862 |
| Urobilinogen |
|
0.004785 | 476.1905 | 4.828 |
Inhibition constants were measured in a 0.046M Tris-HCl, 0.0115M CaCl2, held at a pH 8.1 and 37°C. 10ug/mL of bovine pancreatic trypsin was used with the substrate N-p-Tosyl-Gly-Pro-Arg 7-amido-methylcoumarin HCl stock at 100μM. Each well has a final volume of 150μL: 3μL trypsin, 3μL of inhibitor, 69μL of buffer, 75μL of buffered substrate. The second-order inhibition rate (k2/Ki (M−1s−1)) was generated by carrying out a series of experiments at different concentrations of the potential inhibitory metabolite(s). Non-linear regression modelling was done to determine the IC50 values for the metabolites within the bilirubin deconjugation pathway (n=3 replicates/metabolite).
