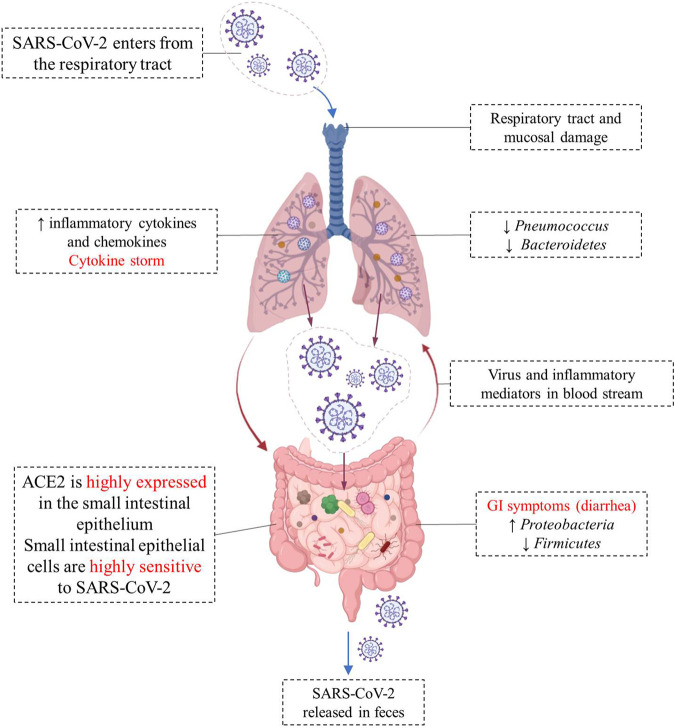
FIGURE 1.
Different changes in the “gut-lung axis” after infection with COVID-19. Respiratory tract infection increases the production of cytokines and chemokines and causes changes in the microbial composition of microflora. Changes in the lung microbiome may cause specific host immune responses. The high expression of ACE2 in the small intestine makes small intestinal epithelial cells highly sensitive to SARS-CoV-2, and the viral infection leads to intestinal malabsorption, secretion imbalance, and diarrhea. SARS-CoV-2 RNA has been detected in fecal sample of COVID-19 patients.