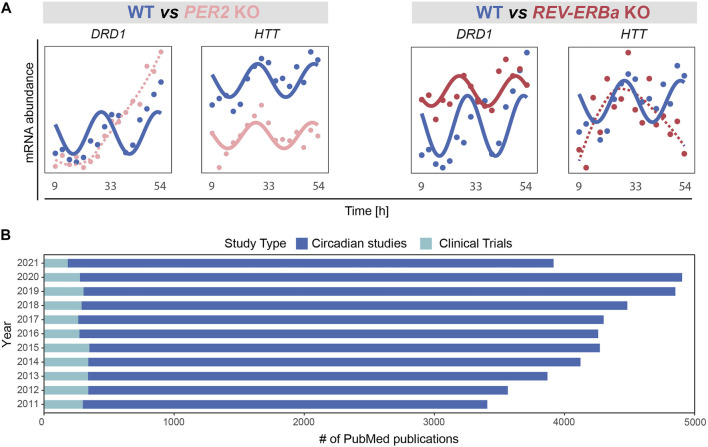
FIGURE 3.
Emerging role of the circadian clock in regulation of disease associated mechanisms and its applications in basic vs. clinical research. (A) Perturbation of core-clock genes in an in vitro CRC model (HCT116 wild type (WT) and their derived PER2 and REV-ERBα knockout (KO) cells, ArrayExpress: E-MTAB-9701 (Yalcin et al., 2021)) may result in complete abolishment of circadian rhythmicity and/or alteration of oscillatory properties (amplitudes or phases), as observed for DRD1, and HTT. (B) Number of PubMed publications in last 10 years. Studies were categorized based on research type: circadian (studies with basic research) and clinical (studies including circadian biology in a clinical study setup).