FIGURE 2.
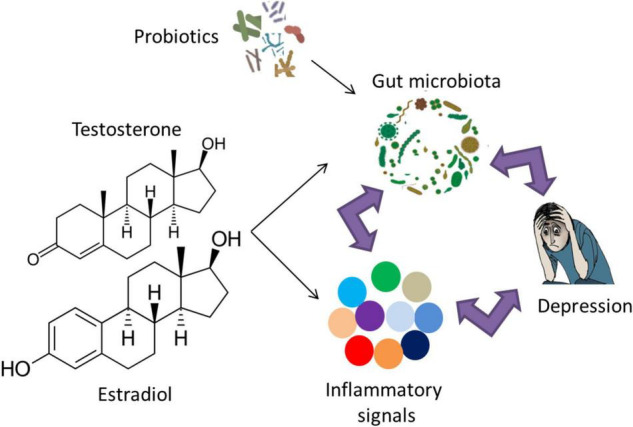
The reciprocal link between gut microbiota, inflammation and depression. The role of probiotic supplementation in turning the gut microbiota composition into a healthier form may lead to normal brain function and alleviation of depressive symptoms via modulation of inflammatory responses. Examples of probiotic genera include Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Lactococcus, Propionibacterium, Bulgaricus, and Streptococcus. Notably, sex hormones affect gut microbiota and/or inflammatory signals, which may play a role in the sex bias of depression.
