Figure 1. Determination of nitric oxide release by sialokinin I.
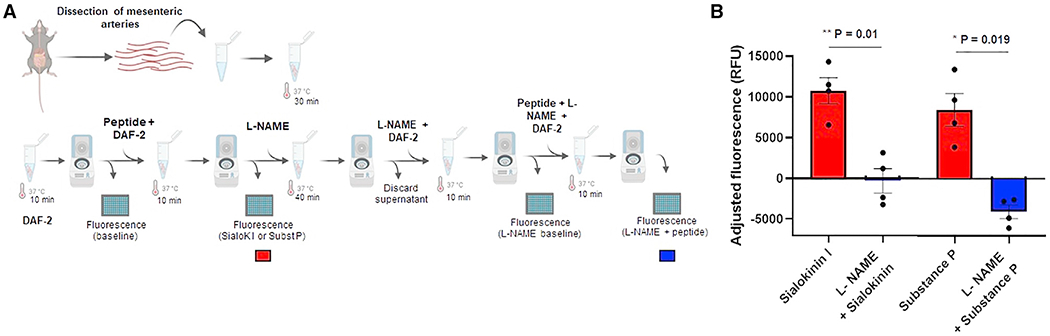
(A) Diagram of the workflow used for the ex vivo detection of NO production by mouse mesenteric arteries.
(B) Graph shows the adjusted fluorescence as relative fluorescence units (RFUs) in the presence of sialokinin I or substance P with (blue) and without (red) l-NAME. The adjusted fluorescence was calculated as the fluorescence at wavelengths Ex485 and Em538 minus the correspondent baseline reading from each set of arteries. Baseline readings were assigned to the fluorescence readouts from arteries incubated with either DAF-2 in KH buffer or l-NAME, DAF-2 in KH buffer for each set of arteries. Each point represents the adjusted fluorescence from ~15 pooled arteries dissected from an individual mouse. Two independent experiments of 2 mice per peptide were included. Bars indicate SEMs. A paired t test was used to determine the statistical significance comparing treatments with or without l-NAME; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
