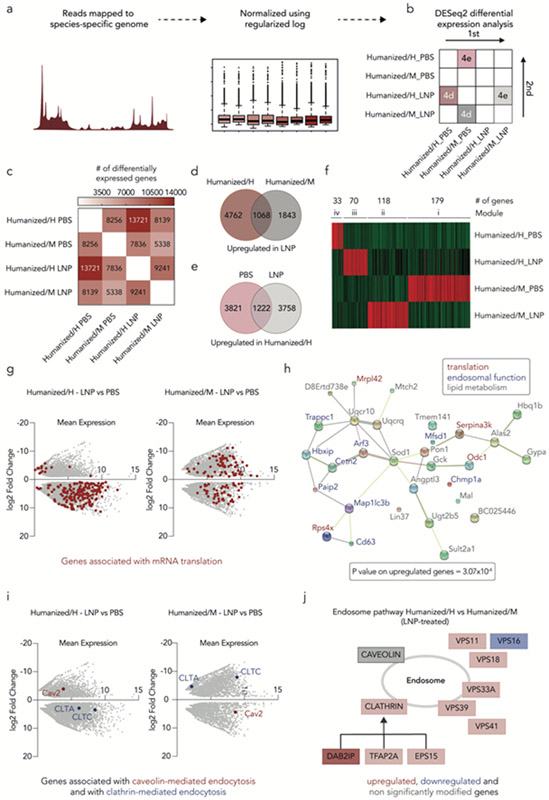
Figure 3.
Transcriptomics studies reveal species-dependent response to LNPs. (a) Schematic of Smart-seq2 protocol design. (b) DESeq2 differential expression analysis uses a pairwise comparison to determine the number of differentially expressed genes between different conditions. (c) DESeq2 differential expression analysis reveals that LNP-treated humanized/H contains the higher number of differentially expressed genes. (d) The number of upregulated genes was determined between both species (humanized/H and humanized/M) after LNP treatment. (e) The number of upregulated genes was determined between the humanized/H LNP-and PBS-treated samples. (f) Weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) shows the 400 most upregulated genes in humanized/H and humanized/M hepatocytes; four unique modules were identified. (g) Differential gene expression in the LNP-treated humanized/H and humanized/M hepatocytes was identified. Genes associated with mRNA translation are highlighted in red. (h) STRING analysis, based on the top 30 upregulated genes, across the LNP-treated humanized/H and humanized/M samples identifies interactions between genes associated with translation, lipid metabolism, and endosomal function. (i) Differential expression of genes associated with caveolin- and clathrin-mediated endocytosis in both humanized/H and humanized/M hepatocytes indicates receptor-mediated endocytosis-related difference in delivery across species. (j) As an additional line of evidence, Reactome database was utilized to illustrate the differences in endocytosis-related gene expression between LNP-treated humanized/H and humanized/M hepatocytes.