Figure 4: Pre-exposure of the gut microbiota to ciprofloxacin in vivo results in differential invasion of S. Typhimurium in vitro.
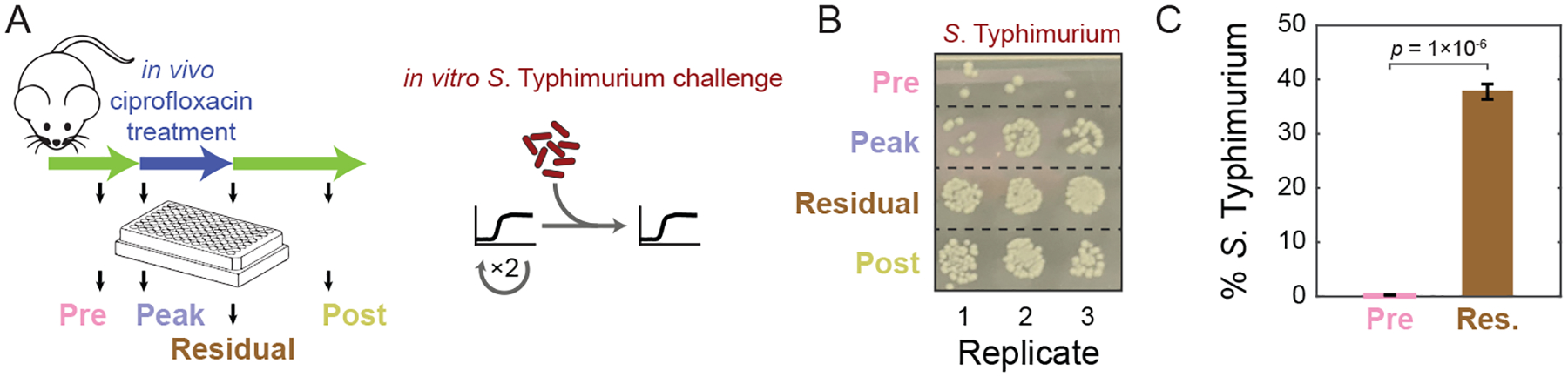
A) Experimental setup for in vitro challenge with S. Typhimurium. SICs passaged in BHI from pre-, peak, residual, and post-treatment humanized mouse fecal inocula were revived after freezing and passaged twice in BHI. SICs were mixed with S. Typhimurium and S. Typhimurium levels were quantified after 48 h of growth.
B) SICs derived from mice treated with ciprofloxacin are more susceptible to S. Typhimurium. Colonies of S. Typhimurium SL1344 after 48 h of growth with SICs diluted 1:104 and grown aerobically on LB+streptomycin.
C) Single-cell quantification of mCherry-tagged S. Typhimurium 14028s after co-culture with SICs derived from pre- and residual-treatment mice fecal inocula. p-value is from a Student’s two-sided t-test; n=3.
