Figure 2.
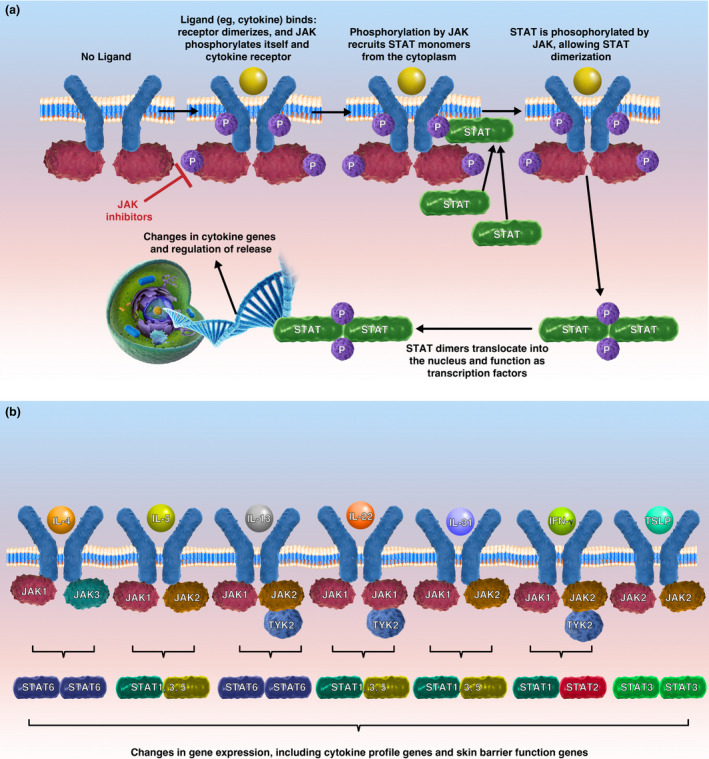
JAK/STAT signalling. (a) Upon ligand binding (e.g. cytokines), the cytokine receptor dimerises, and JAK phosphorylates itself and the intracellular region of the cytokine receptor. Phosphorylation of the receptor recruits STAT monomers from the cytoplasm. JAK phosphorylates STAT, which then forms a dimer. STAT dimers translocate into the nucleus where they act as transcription factors and impact gene expression, including expression of cytokine genes involved in inflammation, epidermal skin barrier, itch and pain. JAK inhibitors interact with the P‐loop of the JAK kinase domain, 148 and hence inhibit events downstream of JAK phosphorylation (JAK, Janus kinase; P, phosphorylation; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription). (b) Key cytokines in atopic dermatitis and the JAK and STAT molecules that mediate signalling (IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin).
