Figure 3.
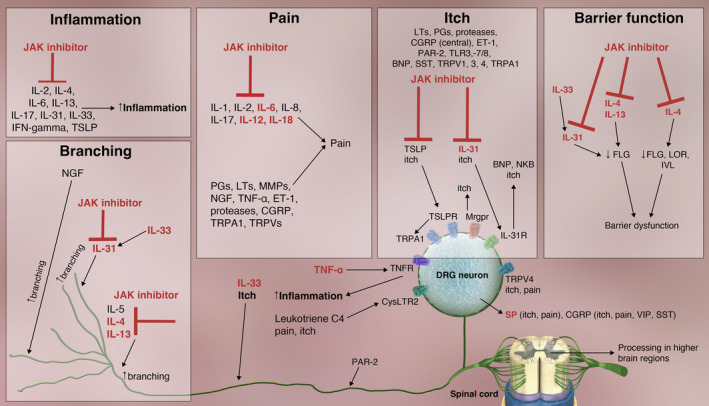
Effects of JAK inhibitors on neuroimmune circuits and barrier dysfunction in atopic dermatitis. Cytokines in red/bold text are upregulated in atopic dermatitis (BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; CGRP, calcitonin gene‐related peptide; CysLTR2, cysteinyl leukotriene receptor; DRG, dorsal root ganglion; ET‐1, endothelin 1; FLG, filaggrin; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IL‐31R, IL‐31 receptor; IVL, involucrin; JAK, Janus kinase; LOR, loricrin; LT, leukotriene; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MrgprX1, Mas‐related G protein–coupled receptor X1; MrgprX2; Mas‐related G protein–coupled receptor X2; MrgprD, Mas‐related G protein–coupled receptor‐D; NGF, nerve growth factor; NKB, neurokinin B; PAR‐2, proteinase‐activated receptor 2; PG, prostaglandin; SP, substance P; SST, somatostatin; TLR, toll‐like receptor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; TRPA1, transient receptor potential ankyrin 1; TRPV, transient receptor potential vanilloid; TSLP, thymic stromal lymphopoietin; TSLPR, thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptor; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide).
