FIGURE 4.
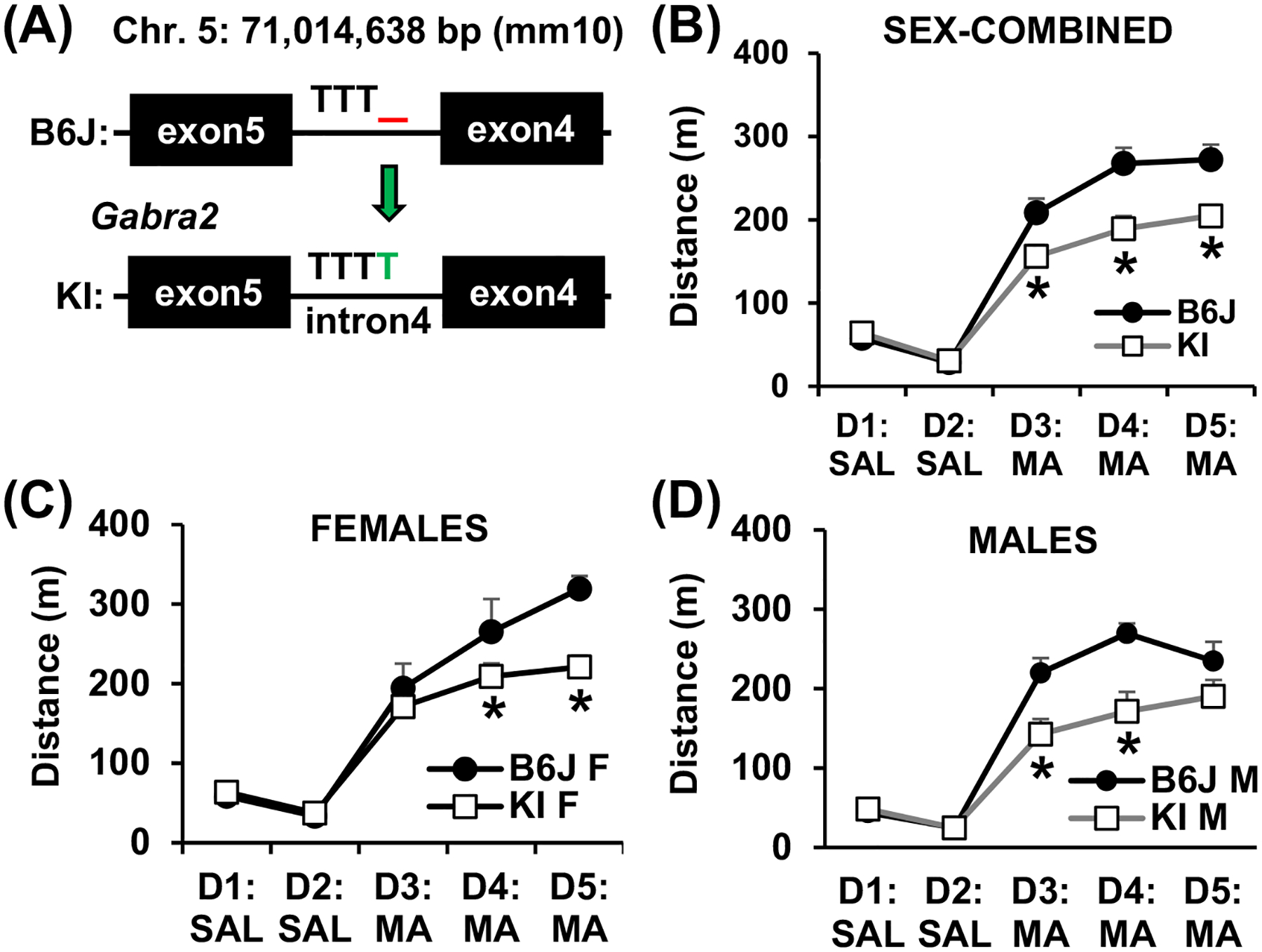
Identification of a quantitative trait variant in Gabra2 that underlies variation in methamphetamine stimulant sensitivity as measured via distance traveled. (A) Schematic of gene-edited knockin (KI) of the single T nucleotide “corrected” allele that was inserted into intron 4 of the Gabra2 gene. The C57BL/6J (B6J) substrain harbors a single nucleotide T deletion on chromosome 5 at 71,041,638 bp (mm10). CRISPR-Cas9 was used to insert the deleted T nucleotide onto the B6J genome thus “correcting” the single nucleotide deletion. (B) Distance traveled across Day(D) 1 through D5 in Gabra2 KI versus B6J wild-types. Simple contrasts of the sex-combined data showed a significant decrease in distance traveled in KI versus B6J mice on D3 (*p = 0.0063), D4 (*p < 0.0001) and D5 (*p = 0.0001). (C) Distance traveled in females. Simple contrasts identified a significant decrease in distance traveled in Gabra2 KI females versus B6J wild-type females on D4 (*p = 0.0498) and D5 (*p = 0.0009). (D) Distance traveled in males. Simple contrasts showed a significant decrease in distance traveled in KI males versus B6J wild-type males on D3 (*p = 0.0016) and D4 (*p = 0.0001), but not on D5 (p = 0.061)
