Fig. 5 |. Therapeutic strategies to target MYC-driven tumours.
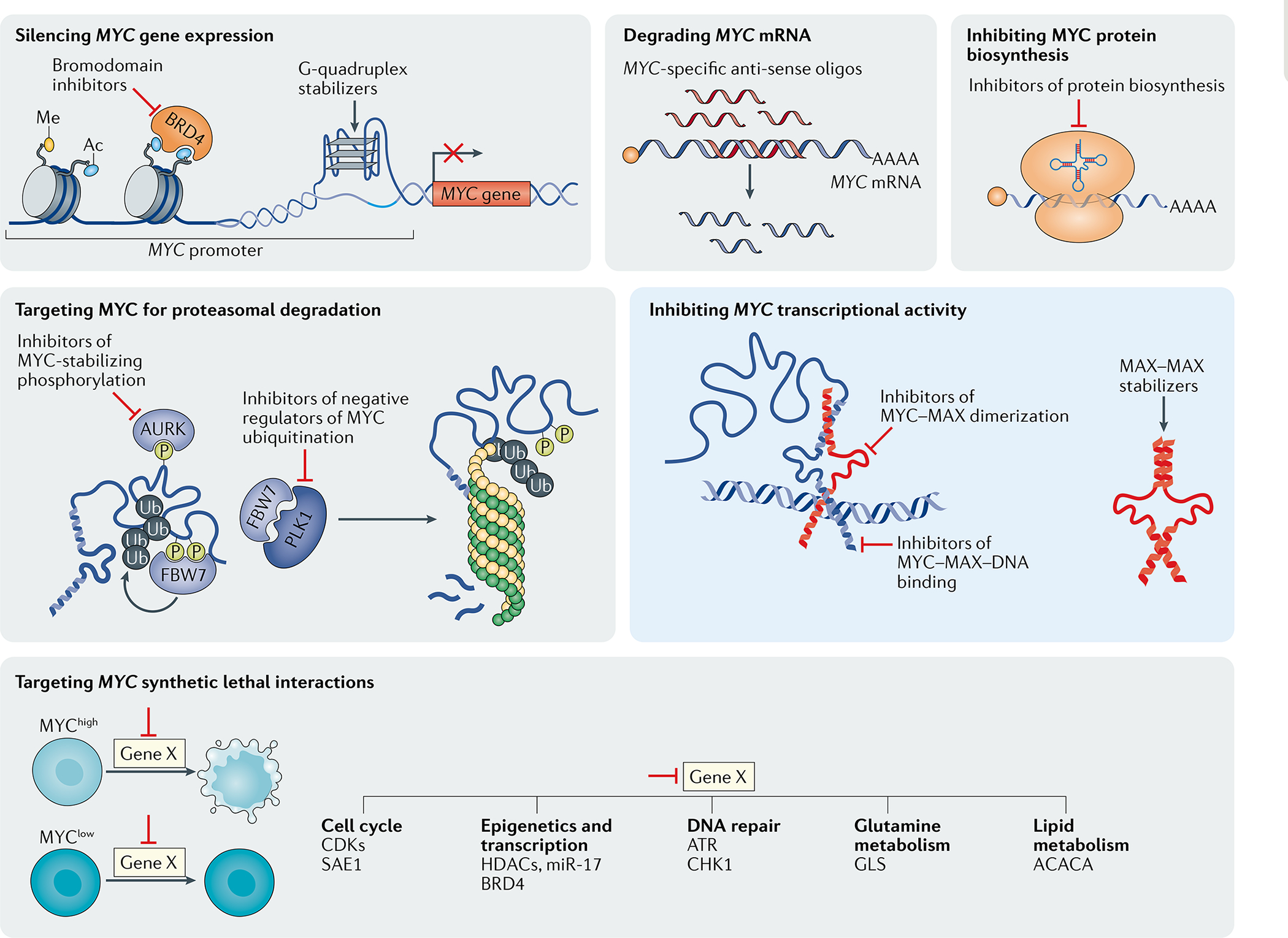
Among the multiple strategies currently explored to target MYC-driven tumours, the majority use indirect approaches (grey boxes) such as those based on inhibiting MYC synthetic lethal genes or interfering with the expression of MYC at the DNA, RNA or protein level. Direct strategies to inhibit MYC (blue box) include approaches using small molecules, peptides or ‘miniproteins’ to inhibit MYC–MAX dimerization, sequester MAX via homodimer stabilization, or interfering with MYC–MAX binding to target DNA sequences. Ac, acetylation; CDKs, cyclin-dependent kinases; HDACs, histone deacetylases; Me, methylation; P, phosphorylation; Ub, ubiquitylation.
