Figure 2.
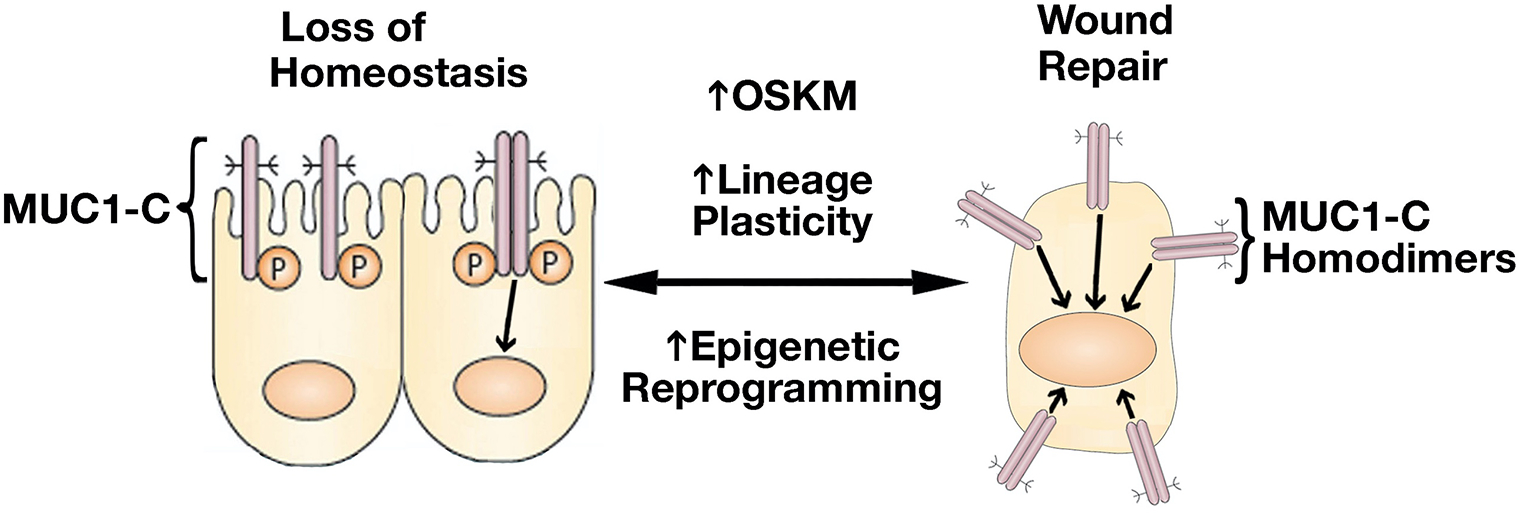
Activation of MUC1-C in response to the loss of homeostasis. Activation of MUC1-C induces homodimers mediated by a redox-sensitive CQC motif in the cytoplasmic domain[22]. MUC1-C homodimers are imported into the nucleus where they interact with transcription factors, such as STAT3, NF-κB, MYC, and E2F, that induce (i) the Yamanaka OSKM pluripotency factors, (ii) lineage plasticity with EMT, and (iii) effectors of epigenetic reprogramming[23,24]. In this way, MUC1-C reversibly couples pluripotency and lineage plasticity with epigenetic reprogramming that govern wound repair.
