Fig. 4 |. Reading out MAGE results.
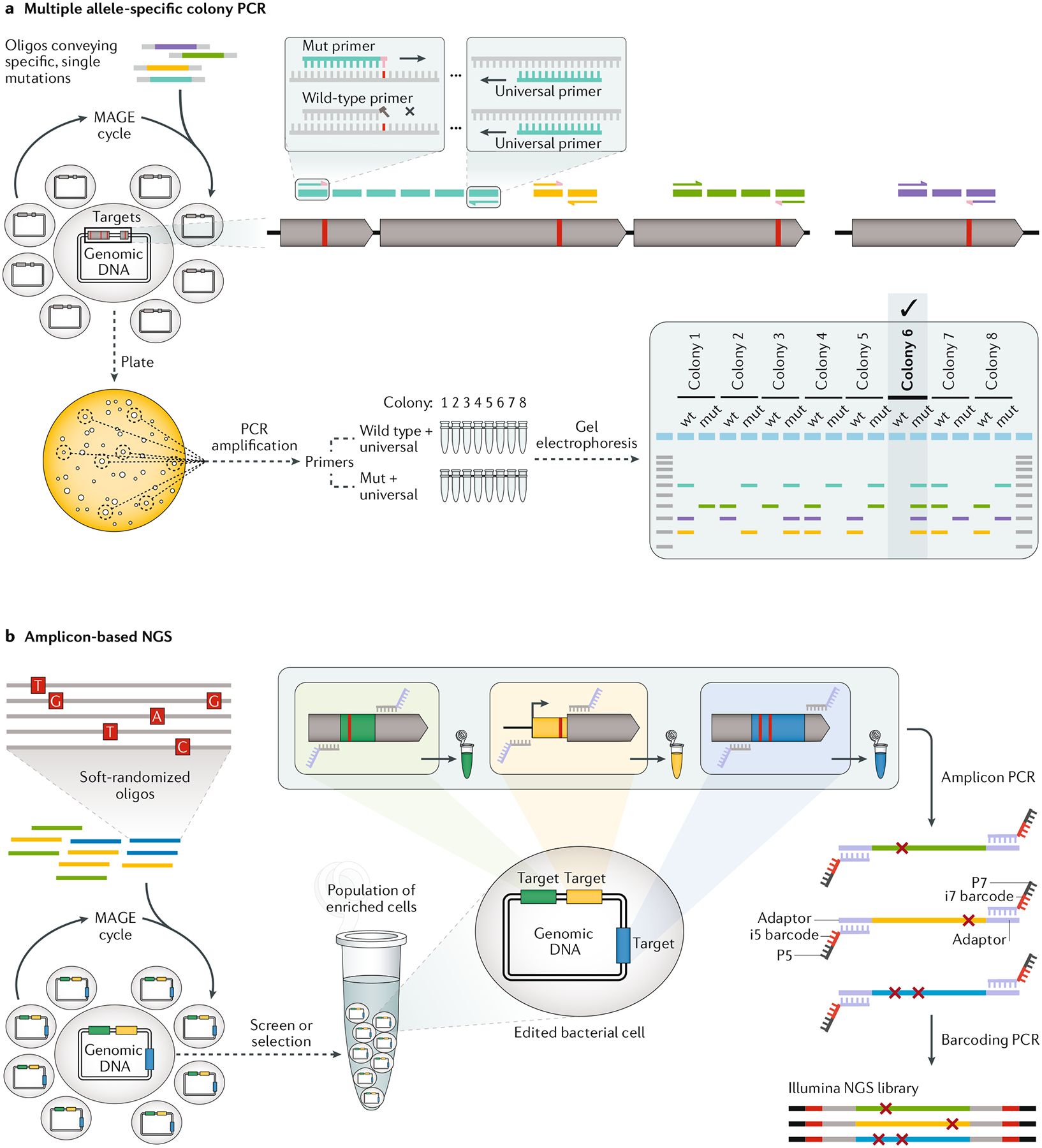
a | Multiple allele-specific colony PCR is a method for quickly identifying edited clonal populations. First, three primers are designed for each targeted modification. Forward primers bind to either the wild-type (wild-type primer) or edited (Mut primer) DNA, whereas a third reverse primer (universal primer) will be paired with both forward primers. Disambiguation is strongest when the 3′-terminal base of the forward primers is designed to anneal to the targeted base modification. Here, the Mut primer is depicted to have a pink terminal base that pairs successfully with the mutated red base, whereas the wild-type primer has a grey terminal base that does not pair, blocking elongation of the primer by DNA polymerase in the PCR reaction. After numerous multiplex automated genome engineering (MAGE) cycles, the edited population is plated out for single colonies, and two separate PCR reactions are run for each colony (wild type + universal and Mut + universal). On an electrophoresis gel, a DNA band should appear only for the allele that is present in the clonal population. Multiple alleles can be combined into a single PCR reaction if the amplicons are designed to have different lengths so that they are easily differentiated by gel electrophoresis. Colony 6, with four mut bands, has successfully incorporated all of the targeted allelic modifications, whereas every other colony shows at least one wild-type band (wt). b | Amplicon-based next-generation sequencing (NGS) for screening and selecting targeted mutations introduced by MAGE-based strategies such as MAGE sequencing or directed evolution with random genomic mutations (DIvERGE; pictured here). Illumina NGS libraries can be easily created in two PCR steps from a population of edited or edited and then enriched cells. First, amplicon PCR mixes a population of cells separately with primers to amplify each targeted locus (green, yellow or blue) and at the same time affix an adapter sequence. Amplicon PCR reactions are run separately for each targeted locus, but the population of cells is pooled in the reaction. Second, barcoding PCR is run on each amplified locus to add primers that bind to the adapter region and affix a unique barcode and sequences for binding to a flow cell. Oligo, oligodeoxynucleotide.
