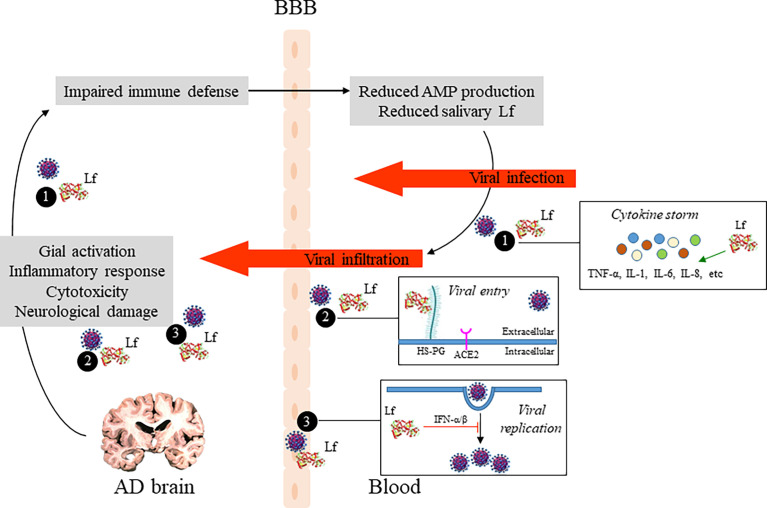
Figure 2.
Potential role of Lf in the relationship between AD brain pathology and COVID-19. Pathogenic events leading to neuronal damage may impair the host defense system which in turn reduce AMP production, including Lf, and influence the extent of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the brain. Additionally, potential antiviral mechanisms of Lf are shown: (1) by modulating SARS-CoV-2 induced inflamation, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, such as IL-6 and TNFα; (2) by occupying binding sites of SARS-CoV-2, as heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) on the host cell surface, reducing viral surfing and subsequent viral entry; and (3) by inhibition of viral replication via induction of intracellular cell signals. AD, Alzheimer’s disease; Lf, lactoferrin; AMP, antimicrobial peptide; BBB, blood-brain barrier.