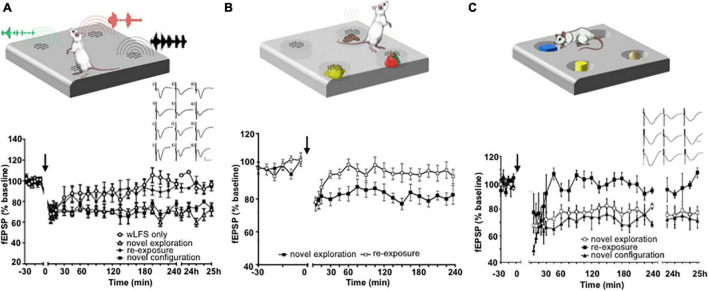
FIGURE 2.
Exposure to item-place experience facilitates the expression of hippocampal LTD. (A) Exploration of novel spatial configurations of auditory items (top) promotes the expression of hippocampal LTD. Graph: weak low frequency stimulation (wLFS, 1 Hz 600 pulses) applied to Schaffer collateral CA1 (SC-CA1) synapses results in short-term depression (STD) in freely behaving rats that lasts for ca. 30 min. Combination of wLFS with novel exploration of audiospatial configurations results in the facilitation of STD into LTD. A subsequent re-exposure to the same items in the same locations at least 7 days after the first exposure during wLFS results in STD. But combining wLFS with the exposure to a novel configuration of the same auditory items results in LTD that lasts for over 24 h. Inset: analogs show examples of field excitatory post synaptic potentials (fEPSPs) recorded prior to wLFS (i), 5 min (ii) and 24 h (iii) after wLFS in animals that received wLFS only (top row), animals that engaged in novel audiospatial cue exploration (2nd row), animals that experienced re-exposure to the cues (3rd row) and animals that were exposed to a novel audiospatial cue configuration (bottom row) Scale bars, vertical: 5 mV, horizontal: 5 ms. From Dietz and Manahan-Vaughan, 2017. (B) Novel Exploration of a spatial configuration of odors (top) also promotes the expression of LTD. The graph shows the expression of LTD when wLFS (applied to SC-CA1 synapses) was combined with de novo exposure to different odors that emanated from holes in the floor of the chamber. Re-exposure to the same odors in the same spatial locations ca. 1 week after the first exposure failed to induced LTD. From André and Manahan-Vaughan (2013). (C) Exploration of spatial configurations of novel visual items promotes LTD (top). Graph: novel exploration of spatially distributed visual items during wLFS of SC-CA1 synapses enables LTD. Re-exposure to the same items in the same spatial configuration during wLFS 1 week later results in STD, whereas exposure to a new spatial configuration of the visual items results in LTD that lasts for over 24 h. Inset: analogs show examples of fEPSPs recorded prior to wLFS (left column), 5 min (middle column) and 24 h (right column) after wLFS in animals that engaged in novel visuospatial cue exploration (top row), animals that experienced re-exposure to the cues (middle row) and animals that were exposed to a novel visuospatial cue configuration (bottom row). Scale bars, vertical: 5 mV, horizontal: 5 ms. From Kemp and Manahan-Vaughan (2004). Cartoons (A–C) were modified from: Manahan-Vaughan (2018b).