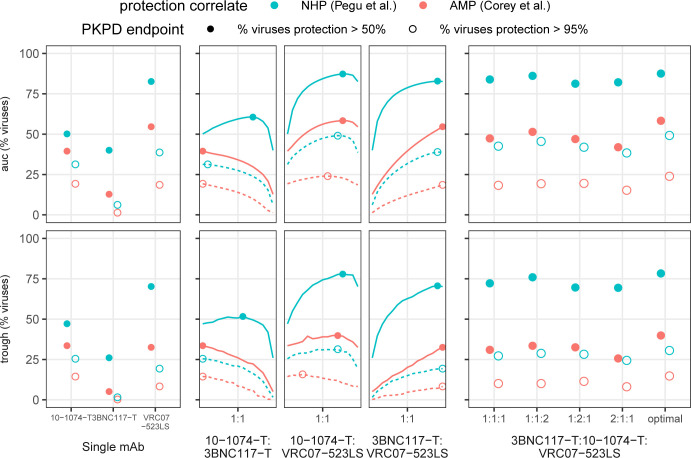
Fig 5. Additional enhancement after optimization of 3-drug therapy.
Using 3 well known anti-HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies, we performed an analysis predicting the percent of viruses covered at more than 50% and 95% protection levels using protection correlates from an NHP meta-analysis(14) and the AMP clinical trials(5). The percent viruses covered were computed over the total time course using area under the curve (auc) and at the final time point (trough). We compared coverage for the bNAbs individually, in dual combination, and in triplicate as 1:1:1, 1:1:2, 1:2:1, 2:1:1, and the optimal combination (see S2 Table). Enhancement over the best single bNAb (VRC07-523-LS) is generated through combinations when evaluating the percent of the viruses neutralized at a 95% level. However, triple drug therapy does not meaningfully enhance over optimized 2-drug therapy levels, even when completely optimized. Protection levels are more optimistically predicted using the NHP meta-analysis vs. the AMP trials (see also S3 Fig), and optimal designs can depend on the underlying protection correlate (e.g., 10-1074-T:VRC07-523LS auc). Indeed, a 1:1:1 3 drug therapy is outperformed by the optimized 2-drug therapy, highlighting the need to carefully perform case-studies for any optimization scenario.