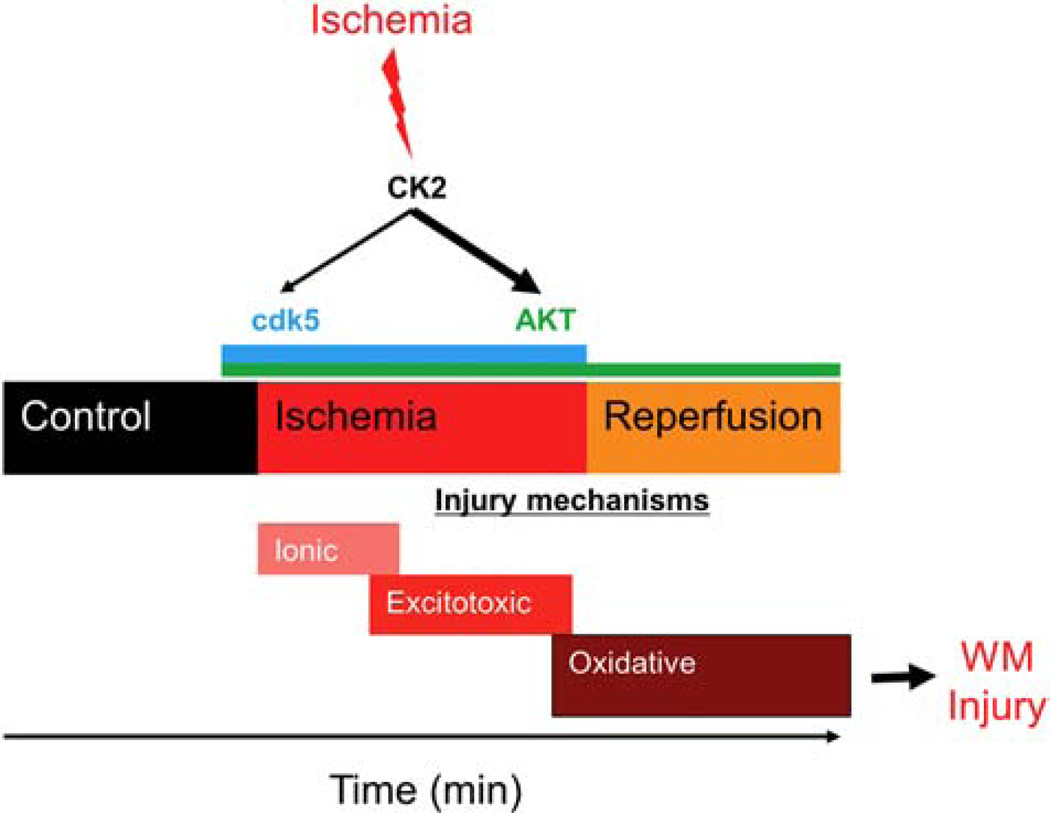
Figure 11. CK2 inhibition confers white matter functional protection against ischemia by differentially regulating the CDK5 and AKT signaling pathways.
Ischemic injury in young WM follows a sequential order initiated by loss of ionic homeostasis leading to excitotoxicity, and then merging into oxidative injury. Our findings suggest that ischemia in WM results in CK2 activation. Functional protection was evident when CX-4945, a CK2 inhibitor, was applied before or after glutamate accumulation, which may suggest that CX-4945 could simultaneously target the excitotoxic and oxidative pathways. CK2 recruits CDK5 and AKT/GSK3β signaling to mediate WM ischemic injury in a spatiotemporal manner such that CDK5 signaling becomes important during ischemia, while AKT signaling emerges as the main pathway during the reperfusion period following ischemia.