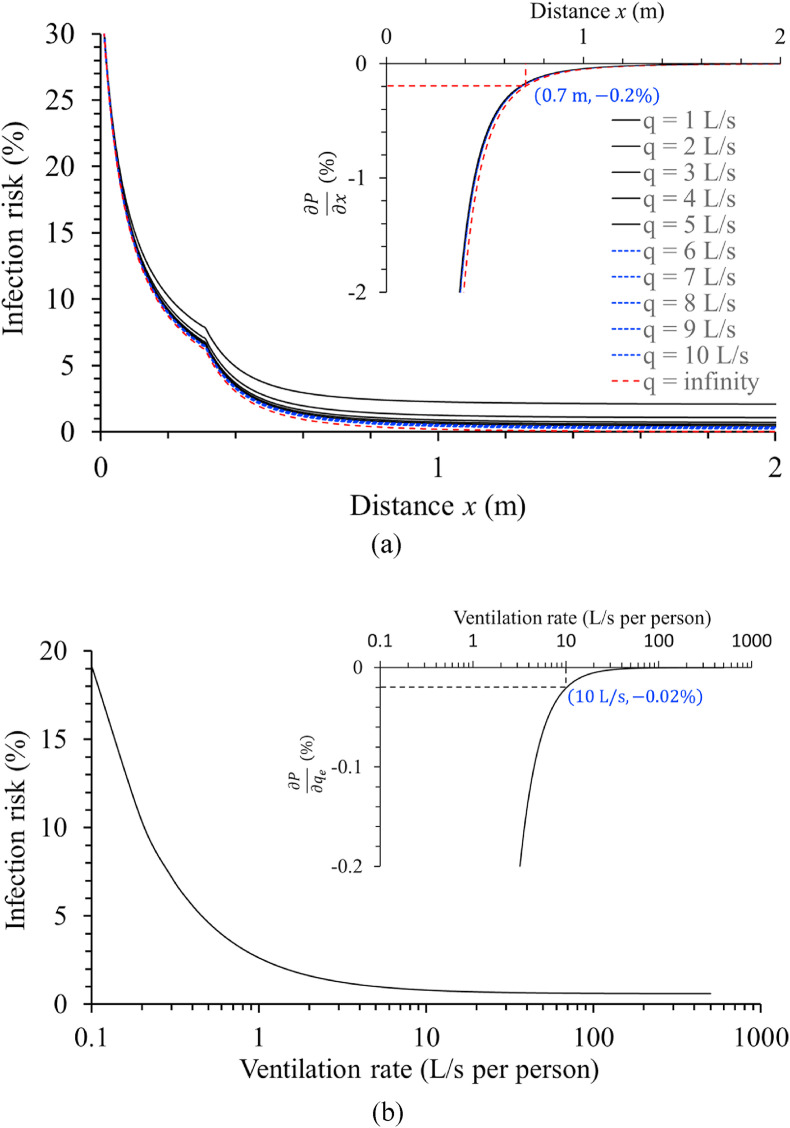
Fig. 11.
Estimated short-range airborne infection risk varies with distance and ventilation rate, and the partial derivatives of infection risk against distance and ventilation rate. (a) Estimated short-range airborne infection risk, , as a function of the distances and ventilation rates for standard activity (infectious quantum concentration, 0.1 quanta/L and exposure time, 42 s, assuming a 2-h total exposure period with four close-contact events per hour and 5.4 s/per close-contact event). In the inserted figure, the partial derivative of infection risk is shown against distance . (b) The estimated short-range airborne infection risk at threshold distance m and, in the inset figure, the partial derivative of infection risk against the ventilation rate are shown.