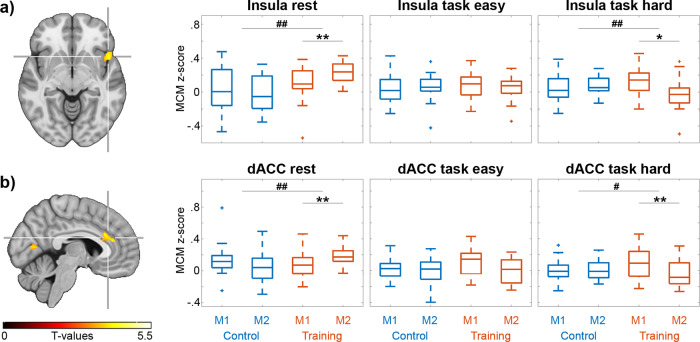
Fig. 3. Learning-induced changes in metabolic connectivity mapping (MCM) with the occipital cortex as target region.
Four weeks of training the video game Tetris® resulted in specific adaptations of connectivity from the right insula (a) and the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC, b) to the occipital cortex (group*time*condition interaction, p < 0.05 FWE-corrected cluster level). Post-hoc comparisons showed that at rest MCM increased for both connections in the training group (n = 21) as compared to the control group (n = 20). In contrast, MCM decreased during the hard task condition in the training group. There were no significant changes in the control group between the two measurements (M1, M2). Furthermore, MCM values between training and control groups at measurement 1 were not significantly different. Boxplots show the MCM z-scores of the clusters indicated by the crosshair. Post-hoc comparisons indicate significant differences for the group*time interaction (#p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01) and for the differences between the two measurements (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01), corrected for multiple comparisons with the Bonferroni-Holm procedure. Boxplots indicate median values (center line), upper and lower quartiles (box limits) and 1.5× interquartile range (whiskers). Data for the plots are provided in Supplementary Data 4–7.