Figure 2.
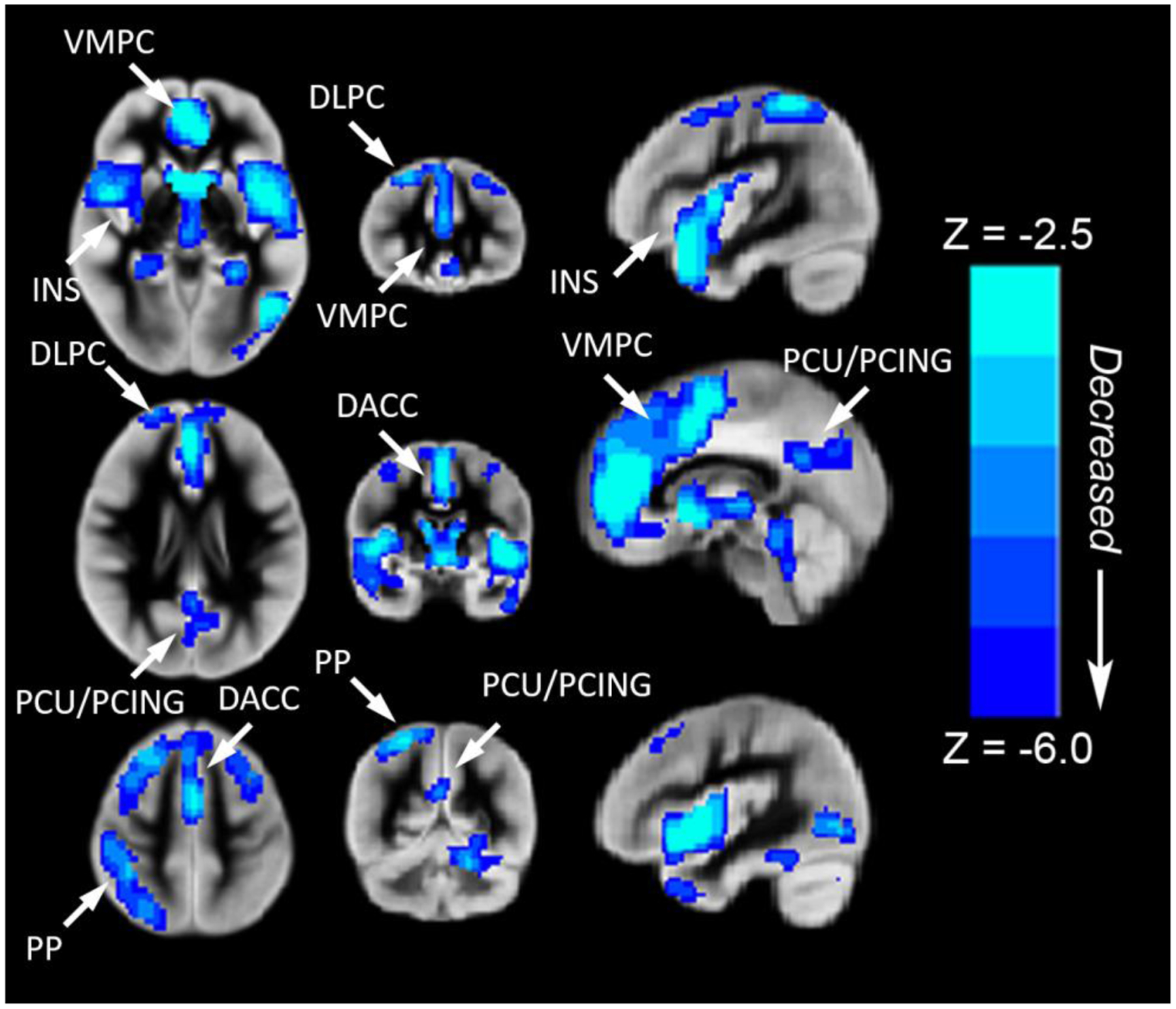
Regions with decreased rCBF (blue voxel color) in children and adolescents with CHD compared to normal controls (voxel-wise group comparison with results projected on one image). Reduced rCBF (controlled for age, gender and maternal education) was seen in the following cortical regions: (1) fronto-medial cortex [ventromedial prefrontal-VMPC (salience network) and dorsal anterior cingulate-DACC (anterior default network)] >fronto-lateral cortex [bilateral dorsolateral prefrontal-DLPC (central executive network)]; (2) parietal-medial cortex [posterior cingulate-PCING and precuneus-PCU (posterior default mode network)] > parietal-lateral cortex [right inferior parietal lobule (central executive network)]; (3) subcortically, in the bilateral insula-INS (salience network) and bilateral caudate. All regions significant at FWE-corrected p < 0.05. Abbreviations: Ventrolateral medial prefrontal cortex (VMPC), Insula (INS), Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPC), Posterior Cingulate (PCING), Precuneus (PCU), Dorsal Anterior Cingulate Cortex (DACC), Posterior Parietal (PP). Images in radiologic orientation.
