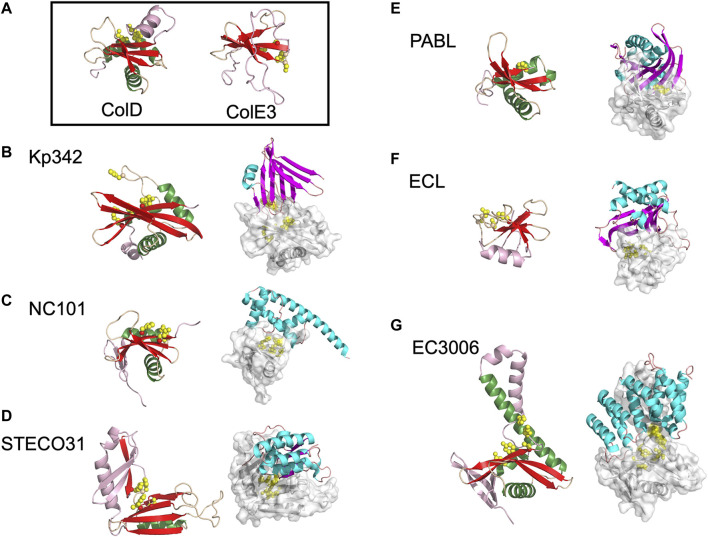
FIGURE 2.
The diverse range of structures for BECR family CdiA-CT toxins and their CdiA-CT/CdiI complexes. (A) As representatives of BECR structural folds we show and box ColD (PDB ID: 5ZNM (Chang et al., 2018)) and ColE3 (PDB ID: 2B5U). ColD and ColE3 are colored as in the left panels described below. CDI BECR toxin and toxin/immunity complex structures are shown from: (B) K. pneumoniae 342 (Kp342) [PDB ID: 6CP9 (Gucinski et al., 2019)], (C) E. coli NC101 [PDB ID: 5I4Q (Jones et al., 2017)], (D) E. coli STEC_O31 [PDB ID: 5HKQ (Michalska et al., 2018)], (E) P. aeruginosa PABL017 [PDB ID: 6D7Y (Allen et al., 2020)], (F) E. cloacae ATCC 13047 (ECL) [PDB ID: 4NTQ (Beck et al., 2014)], and (G) E. coli 3006 (CdiA-CT/CdiIEC3006) [PDB ID: 6CP8 (Gucinski et al., 2019)]. For each pair, the left panel displays the toxin alone in cartoon representation with its BECR core structure colored by secondary structure with β-strands in red, α-helices in green, and loops in wheat, and the remainder of the secondary elements are colored in light pink. Active site residues are shown as yellow spheres. In the right panel is the CdiA-CT/CdiI complex with CdiI colored by secondary structure: β-strands in magenta, α-helices in cyan, and loops in salmon. CdiA-CT has a semi-transparent molecular surface with white cartoon representation and with active site residues shown as yellow spheres.