FIGURE 3.
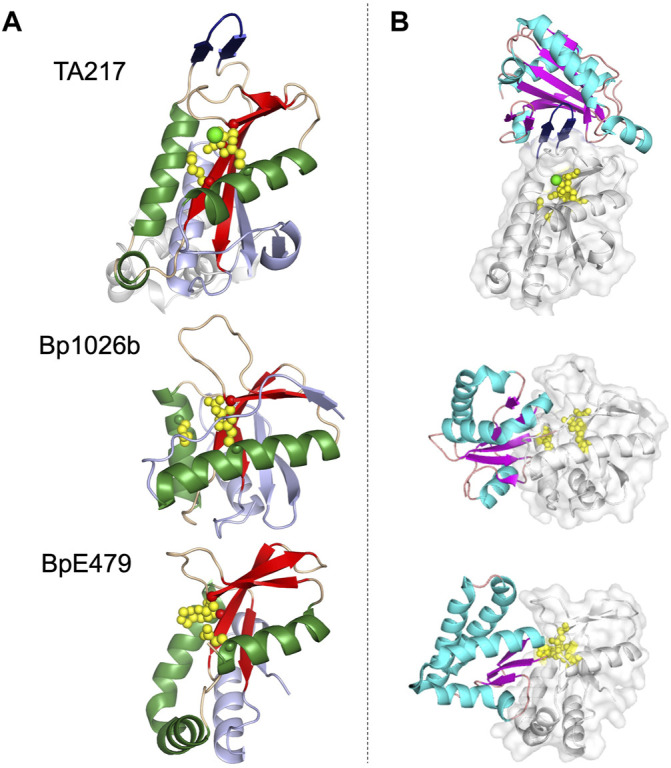
Representative structures of the PD-(D/E)XK family CdiA-CT toxins and CdiA-CT/CdiI complexes from E. coli TA271 (CdiA-CT/CdiITA271) [PDB ID: 4G6U (Morse et al., 2012)], B. pseudomallei 1026b (CdiA-CT/CdiI1026b) [PDB ID: 4G6V (Morse et al., 2012)], and B. pseudomallei E479 (CdiA-CT/CdiIE479) [PDB ID: 5J4A (Johnson et al., 2016b)]. (A) CdiA-CT in cartoon representation with the core PD-(D/E)XK structure colored by secondary structure with β-strands in red, α-helices in green, and loops in wheat, and the remainder of the secondary elements colored in light blue. Notably, the structure of TA271 includes additional structure at the N-terminus (gray) domain, a Zn2+ ion (green sphere), and the TA271 core is interrupted by a protruding β-hairpin (dark blue). (B) Structures of PD-(D/E)XK family CdiA-CT/CdiI complexes. CdiI is colored by secondary structure: β-strands in magenta, α-helices in cyan, and loops in salmon. CdiA-CT is in white cartoon representation with a semi-transparent molecular surface and active site residues shown as yellow spheres. In the TA271 complex the bound metal ion and the TA271 β-hairpin are colored as in the toxin alone. The extra N-terminal region of TA271 is omitted.
