Figure 4.
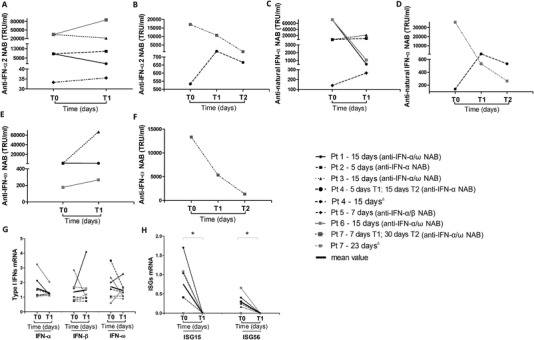
Persistence of anti‐IFN‐I NAB and inhibition of IFN‐related genes in COVID‐19 patients. Temporal changes in anti‐IFN‐α2, anti‐natural IFN‐α, and anti‐IFN‐ω NAB titers and mRNA levels of IFN‐I (IFN‐α, IFN‐β, IFN‐ω), ISG15 and ISG56, measured by antiviral bioassay and RT‐real time PCR, respectively, in COVID‐19 patients (n = 7) at different time points after hospitalization. Each patient is represented by a distinct line. The interval time expressed in days elapsed between T0 (time of hospitalization) and T1 (Panels A, C, and E) and between T0, T1, and T2 (Panels B, D, and F) is indicated for each patient near the corresponding line together with the NAB status. In Panel H, levels of ISGs measured at T1 were undetectable (Ct values < 45). For the statistical analysis levels of ISG15 and ISG56 related to β‐glucuronidase were calculated using 2−Δ Ct method assuming the Ct value as 45 Ct. Statistical analysis were performed using Wilcoxon test. ∗ p = 0.0002. Δ Longitudinal observation of IFN‐I and ISGs levels of Pt 4 and Pt 7 are reported in Panels G and H.
