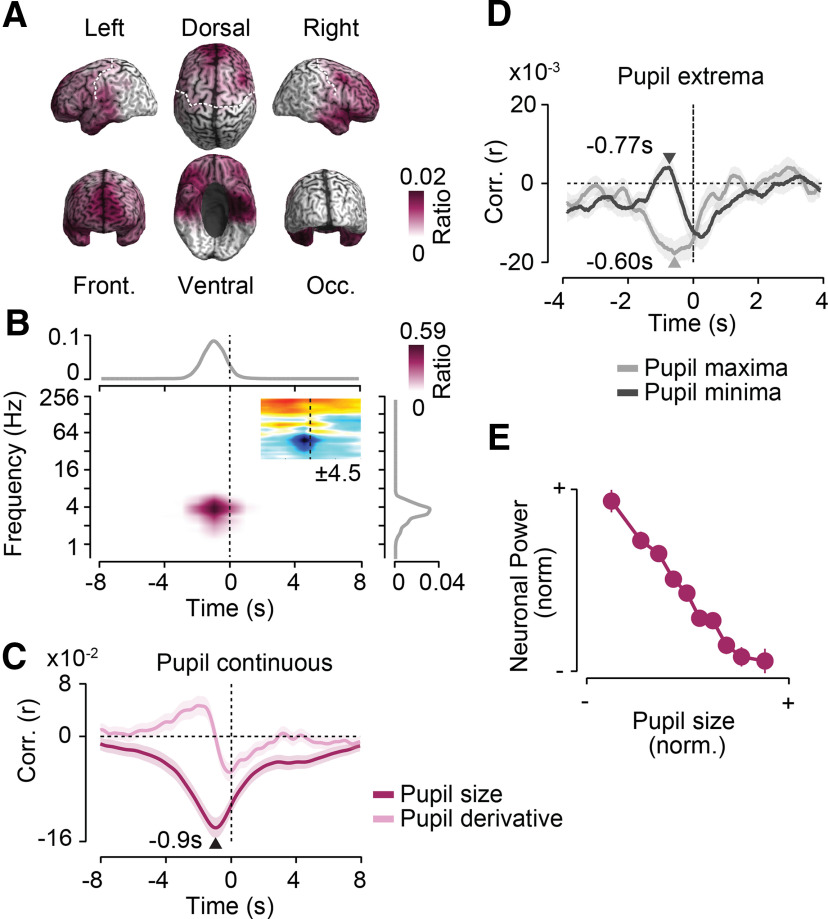
Figure 3.
Frontal 4 Hz activity predicts pupil dilations. Results for a first cluster of negative cross-correlations between power and pupil size as shown. A, Cortical distribution of in-cluster ratios across time and frequencies. For each cortical location, the in-cluster ratio is the ratio of time points and frequencies that are included in the cluster. B, In-cluster ratios across sources (middle), across cortical locations and frequencies (top), and across locations and time (right). In-cluster ratios are the ratio of cortical locations (middle), locations and frequencies (top), and locations and time (right) that are included in the cluster. The small inset in the middle shows the time–frequency distribution of the cross-correlation of pupil size and cortical population activity within the frontal cluster. Colors indicate average t values across subjects (n = 41; maximum/minimum color scale of t values below inset; same time–frequency space as the main panel). C, Temporal cross-correlation of in-cluster power with pupil size and with the temporal derivative of pupil size. D, In-cluster power relative to time points of maximum and minimum pupil size expressed as a correlation coefficient. Arrows indicate the times of statistically compared peak correlations. E, Average normalized pupil size and normalized in-cluster power within each 10% of the normalized pupil size. In-cluster power is shifted 0.9 s forward in time relative to pupil size. All shaded regions and error bars denote the SEM across subjects (n = 41).