Figure 1.
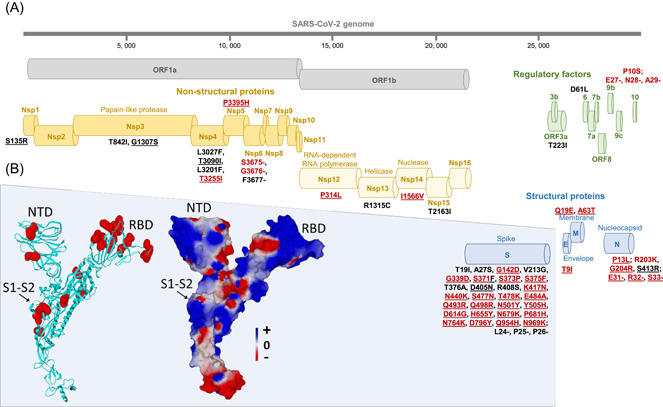
Map of the Omicron 21L/BA.2 spike protein with signature amino acid substitutions and deletions (A) and structural features of 21L/BA.2 Omicron variant spike protein (B). (A) Amino acid substitutions and deletions shared with the 21K/BA.1 Omicron variant are indicated by a red font. Amino acid substitutions and deletions shared with the 21M/BA.3 Omicron variant are underlined. See also Table 1B. (B) Structural model of the Omicron 21L/BA.2 spike protein with mutations highlighted in red atomic spheres (left panel) or in electrostatic surface rendering (right panel). Note the flat surface of the N‐terminal domain that faces lipid rafts of the host cell membrane. The S1–S2 cleavage site is indicated by an arrow. The color scale for the electrostatic surface potential (negative in red, positive in blue, neutral in white) is indicated. NTD, N‐terminal domain; RBD, receptor‐binding domain
