Figure 2.
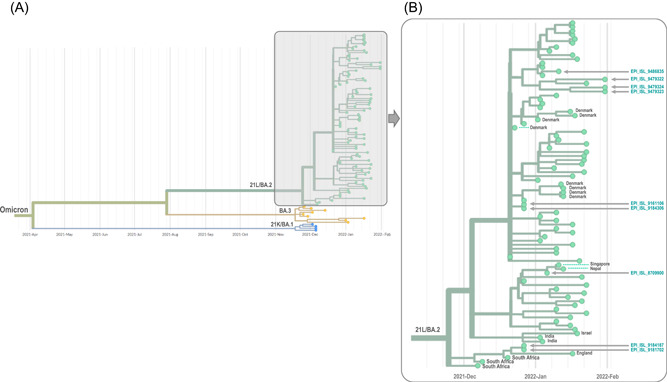
Phylogeny reconstruction based on genomes of the 21L/BA.2 Omicron variant were obtained in the present study. (A) incorporated genome sequences of 21K/BA.1, 21L/BA.2, and BA.3 Omicron variants. (B) is a zoom of the 21L/BA.2 Omicron cluster of (A). Phylogenetic tree was built using the nextstrain/ncov tool (https://github.com/nextstrain/ncov) then visualized with Auspice (https://docs.nextstrain.org/projects/auspice/en/stable/). X‐axis shows time. The 21L/BA.2 Omicron genomes the closest genetically to those obtained in our institute were selected using the Usher tool (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgPhyloPlace) and the GISAID BLAST tool (https://www.epicov.org/epi3/) and they were incorporated in the phylogenetic analysis in addition to all 21L/BA.2 Omicron variant genomes from France are available in GISAID as of 02/02/2022. Sequences obtained in our laboratory (IHU Méditerranée Infection) are indicated by a dark blue arrow and their GISAID identifier is indicated. Countries are indicated when they are not France. Gisaid hcov‐19 acknowledgment table is provided as supplementary file.
