Figure 7.
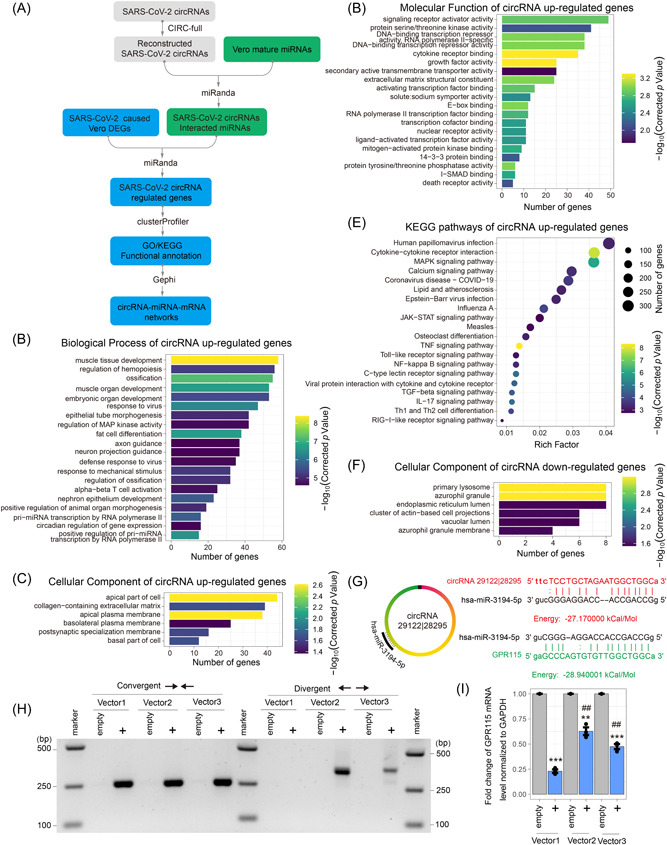
Potential severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) circular RNAs (circRNAs) function in the competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) coregulatory network. (A) Schematic diagram of potential SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs ceRNA coregulatory network analysis method. (B–D) The Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs competitive differentially expressed genes (DEGs). It shows the top 20 significantly enriched GO terms including Biological Process of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs associated upregulated genes (B), cellular component of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs associated upregulated genes (C), and molecular function of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs associated upregulated genes (D), and cellular component of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs associated downregulated genes (E). (F) Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNAs associated upregulated genes. (G) Schematic of hsa‐miR‐3194‐5p‐binding sites and the sequences of SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNA 29122 | 28295 and GPR115. (H) Inverse reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT‐PCR) with divergent primers targeting SARS‐CoV‐2 circRNA 29122 | 28295 and convergent primers and targeting both linear RNA 28295–29122and circRNA 29122 | 28295. (I) The messenger RNA (mRNA) expression levels of GPR115 using quantitative real‐time PCR. Vector1, pcDNA3.1 (linear RNA‐overexpressed Vector); Vector2, pcD‐ciR (circRNA‐overexpressed Vector); Vector3, pcDNA3.1 CircRNA mini (circRNA‐overexpressed Vector); empty, empty Vector. Two‐tailed unpaired t test. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 circRNA 29122 | 28295 versus empty Vector; ##p < 0.01 pcD‐ciR or pcDNA3.1 CircRNA mini versus pcDNA3.1.
