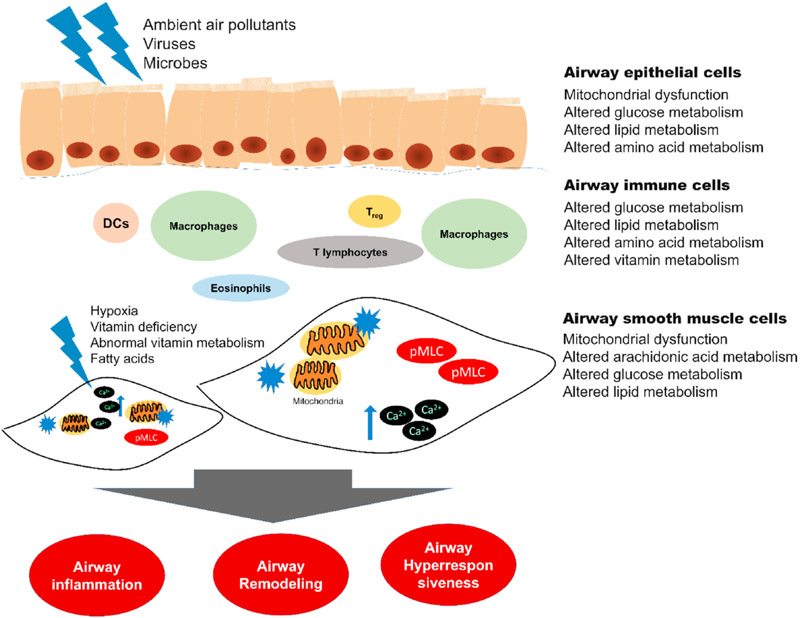
Fig. 2. Cell types and their metabolic roles in asthma.
Each tissue in lungs plays its unique role in asthma pathology. Each tissue is composed of differentiated cell types, homogeneous or heterogeneous, with critical functions. In these cells, altered mitochondrial functions and metabolism of macro- and micro-nutrients -elaborated in the main text- modulate the specialized cellular functions. Airway smooth muscle (ASM) cells primarily dirve bronchial spasm in asthma, which is charaterized by increased cytosolic Ca2+ and myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation. Asthma is characterized by airway inflammtion, remodeling, and hyperresponsiveness. DC - dendritric cells, Treg - regulatory T-lymphocytes, Ca2+ - cytosolic Ca2+, pMLC - phosphorylated myosin light chain.