Figure 4. PARPi induces gaps and sensitizes cells regardless of HR and fork protection (FP) proficiency.
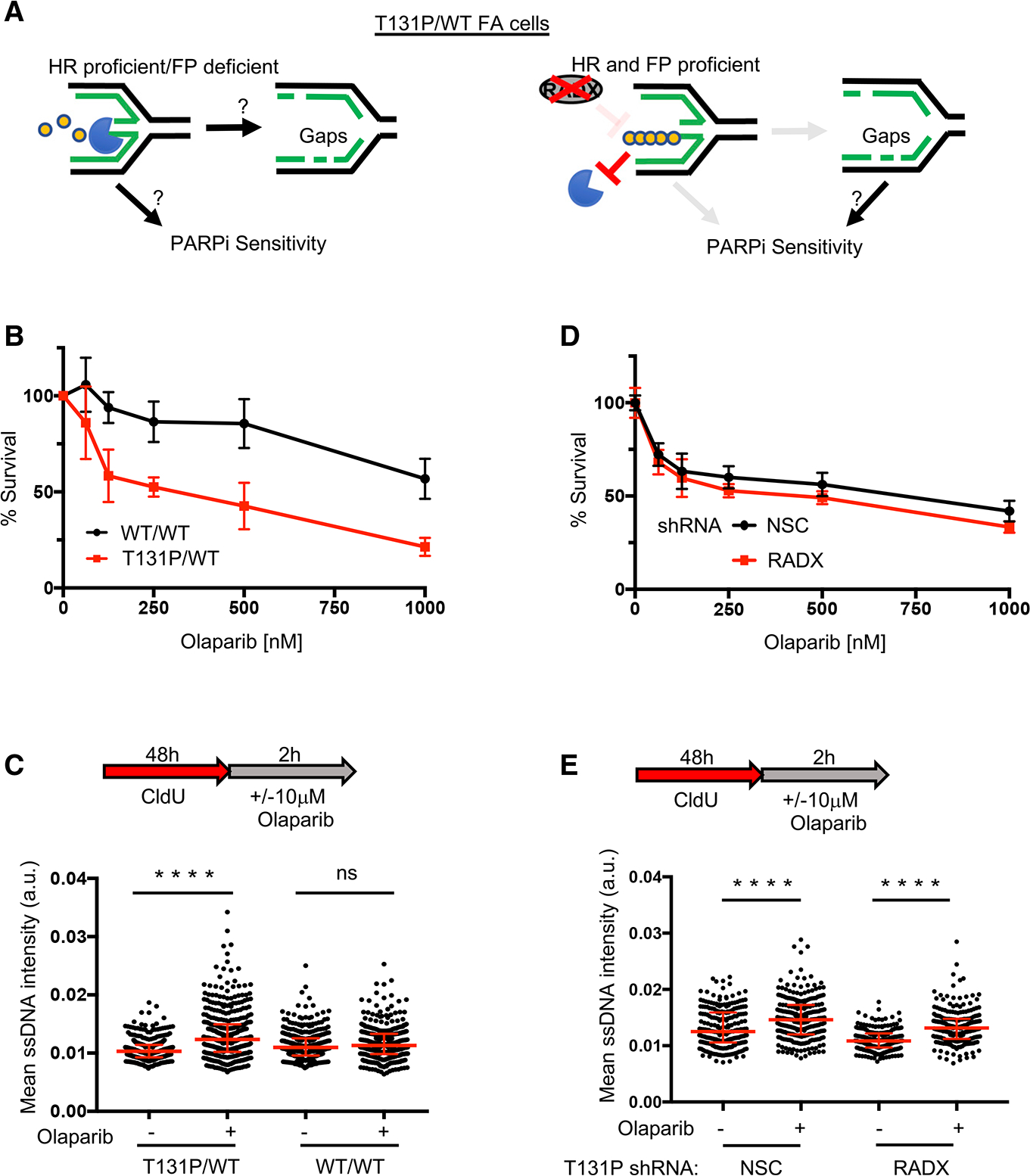
(A) Left: is fork degradation the cause for gaps and PARPi sensitivity in HR-proficient cells? Right: model indicating that PARPi-induced gaps still sensitize cells when FP is restored by depleting RADX.
(B) Cell survival assays for patient fibroblasts (RA2630) RAD51 T131P (T131P/WT) and RAD51 double-allele CRISPR-corrected (WT/WT) cells under increasing concentrations of olaparib.
(C) Schematic and quantification of mean ssDNA intensity for indicated cell lines in (B) following CldU pre-labeling and olaparib release (10 μM, 2 h).
(D) Cell survival assays for indicated cells under increasing concentrations of olaparib. For all cell survival assays, data represent the mean percentage ± SD of survival for each dot.
(E) (E) Quantification of mean ssDNA intensity for indicated cell lines following CldU pre-labeling and olaparib release (10 μM, 2 h). For (C) and (E), red bars represent the median ± interquartile range. At least 200 cells are quantified from 2 biological independent experiments. All statistical analysis according to Kruskal-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s test. ****p < 0.0001.
