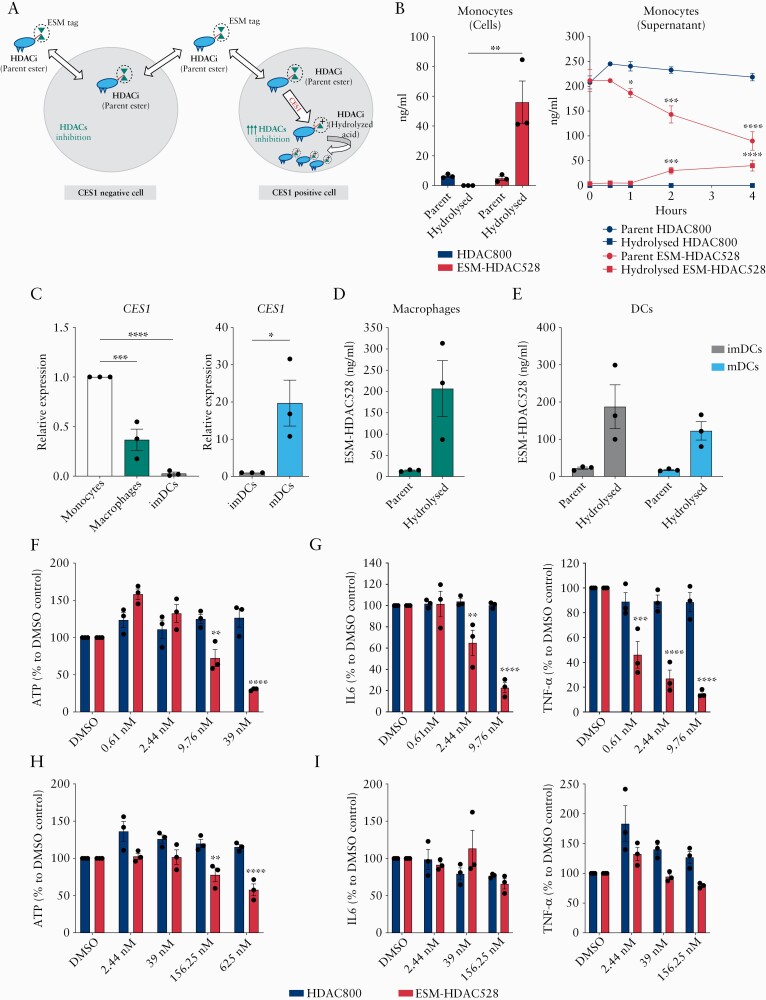
Figure 1.
Profiling ESM-HDAC528 accumulation and anti-inflammatory effect in mononuclear myeloid cell subsets. [A] Schematic diagram of ESM technology for CES1-based targeted drug delivery to mononuclear myeloid cells; ESM-tagged HDACi [parent ester] can freely move in and out CES1- cells but, once it enters CES1+ cells, it is hydrolysed by CES1 to the ESM-HDACi [hydrolysed acid] form of the compound which cannot leave the cells and is retained intracellularly, causing augmented HDACs inhibition. [B] Monocytes were incubated for 4 h with ESM-HDAC528 or non-hydrolysable HDAC800; the parent ester and hydrolysed acid of both compounds were measured both intracellularly and in the supernatant by LC-MS/MS. [C] CES1 mRNA expression in CD14+ monocytes, monocyte-differentiated macrophages and dendritic cells [imDCs], and LPS-polarised dendritic cells [mDCs]. [D and E] Macrophages imDCs or mDCs were all incubated with ESM-HDAC528 for 4 h; the intracellular parent ester and its hydrolysed acid concentrations were measured by LC-MS/MS. [F and G] CD14+ isolated monocytes or [H and I] macrophages differentiated from the same donors were pre-incubated with ESM-HDAC528 or HDAC800 and stimulated for 1 day with LPS, and then ATP production, IL-6, and TNF-α secretion were measured. Data are represented as mean with SEM of three donors, two technical replicates for each. In [B, right panel], parent or hydrolysed forms of HDAC800 and ESM-HDAC528 were compared. In [F to I], similar doses of ESM-HDAC528 and HDAC800 treatment were compared. Statistical testing was performed using two-way ANOVA test [B,E,F,G,H,I] or one-way ANOVA or Student’s t test [C]; *p ≤0.05, **p ≤0.01, *** p ≤0.001, **** p ≤0.0001. SEM, standard error of the mean.