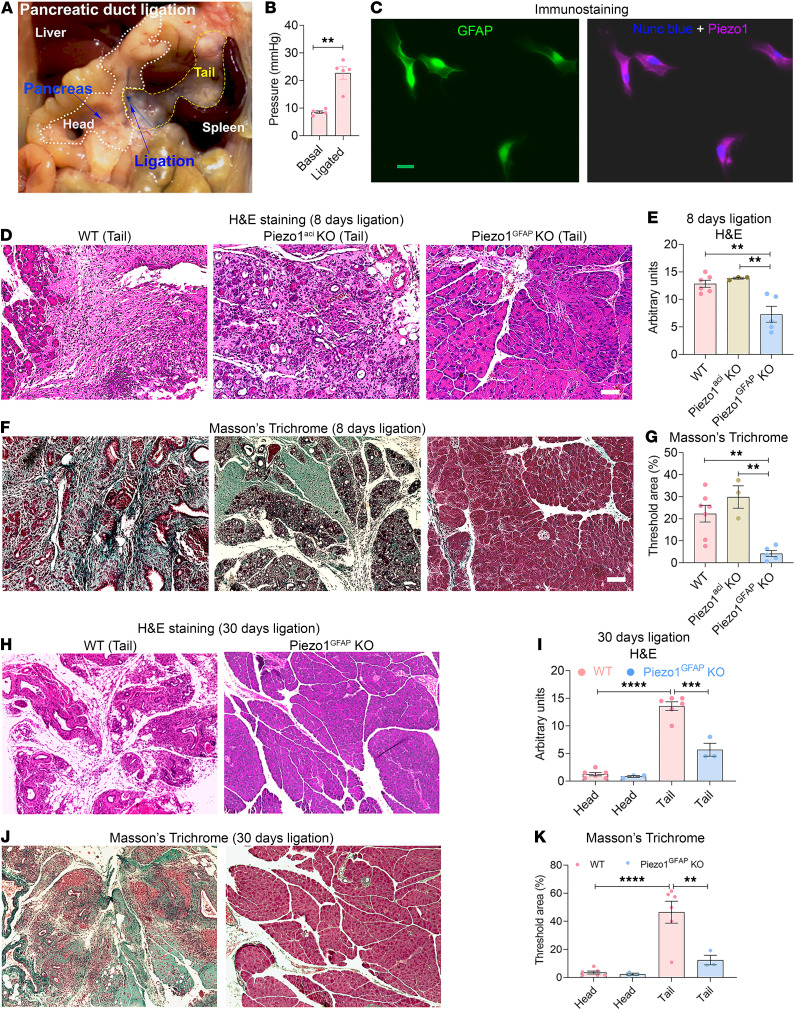
Figure 1. Piezo1GFAP-KO mice were protected from pancreatic duct ligation–induced fibrosis.
(A) Photograph of pancreatic duct ligation (PDL) at the tail region of the pancreas. The head and tail regions of the pancreas are outlined in white and yellow, respectively. (B) Pressure in the tail region of the pancreas before and 5 minutes after pancreatic duct ligation. (C) Immunostaining of GFAP and Piezo1 in mouse PSCs. (D–G) Eight days after PDL, chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis parameters included (D) tail region H&E staining, (E) tail region H&E score, (F) tail region Masson’s trichrome staining, and (G) tail Masson’s trichrome area of WT, Piezo1aci-KO, and Piezo1GFAP-KO mice (n = 3–7). (H–K) Thirty days after PDL, chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis parameters included tail region (H) H&E staining, (I) H&E score, (J) tail region Masson’s trichrome staining, and (K) Masson’s trichrome area of WT and Piezo1GFAP-KO mice (n = 3–6). Statistical analyses were calculated using 2-tailed Student’s t test for 2 groups, and multiple groups were analyzed by 1-way ANOVA. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001. Scale bar: 100 μm.