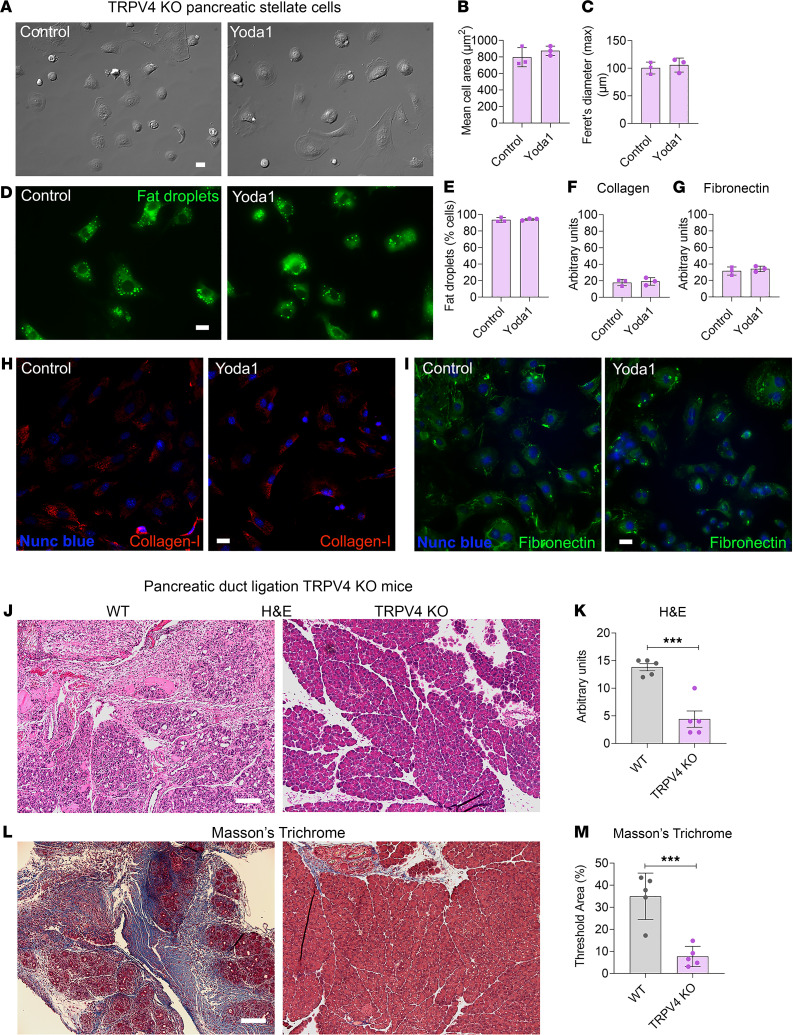
Figure 7. TRPV4-KO mice were protected from pancreatic duct ligation–induced fibrosis.
(A and D) DIC and Bodipy 493/503–stained images of PSCs from TRPV4-KO mice 24 hours after Yoda1 (25 μM). (B and C) Mean cell area and Feret’s diameter (max) of PSCs 24 hours after Yoda1 (25 μM) (from 3 experiments with 20 cells each). (E) Loss of fat droplets in PSCs following Yoda1 (25 μM) (from 3 experiments and > 100 cells). (F and G) Quantification of collagen type I and fibronectin immunostaining in PSCs from TRPV4-KO mice 4 days after Yoda1 (25 μM). (H and I) Representative images of collagen type I and fibronectin staining for the data shown in F and G. (J–M) Pancreatic duct ligation (PDL) at the tail region of the pancreas induced chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis in WT and TRPV4-KO mice. Eight days after PDL, chronic pancreatitis and fibrosis parameters of the tail region included (J) H&E staining, (K) H&E score, (L) Masson’s trichrome staining, and (M) area of WT and TRPV4-KO mice (n = 5). Statistical comparisons were made using 2-tailed Student’s t test. ***P ≤ 0.001. Scale bar: 100 μm.