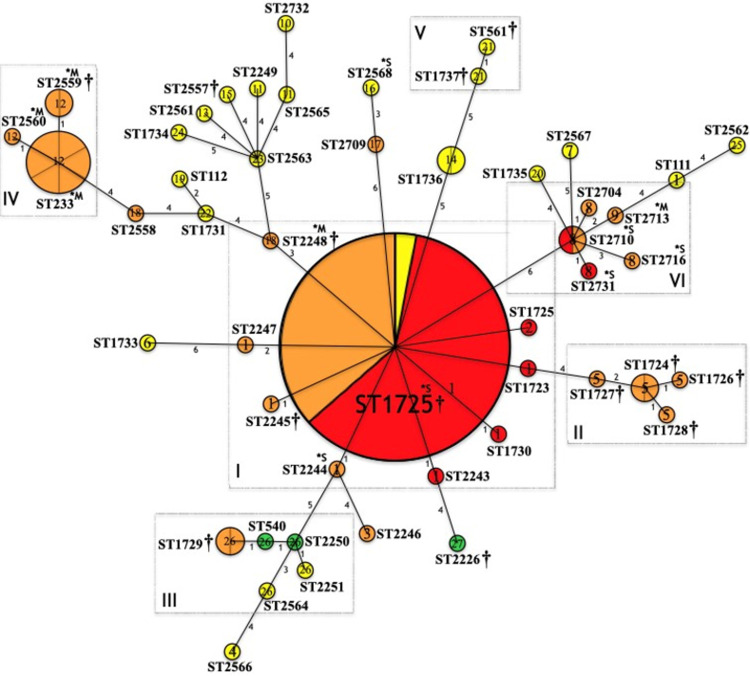
Fig 2. Phylogenetic network based on the MLST genotyping of the P. aeruginosa strains (ST/haplotypes/resistance).
Relationship between the mexR-nalC-nalD haplotypes, the STs and, the susceptibility profiles are shown. P. aeruginosa isolates (n = 91, 48 STs, 27 mexR-nalC-nalD haplotypes). Circles represent sequence types (STs); Circumference is based on ST frequency; Two or more strains with the same ST, including ST1725 are depicted as fractions in each circle (n = 34 strains); Lines connect locus variants; Numbers indicate the number of locus variants among the connected STs. Clonal complexes (CC) formed are highlighted in rectangles and described as I, II, III, IV, V and, VI. STs not grouped into a CC are considered singletons (>3 locus variants with other STs). Number inside the circles (1–27) corresponds with the mexR-nalC-nalD haplotype and are colored differently. †: Fatal patient outcome. Susceptibility profiles: S (green), sensitive; MDR (yellow), multidrug resistant; XDR (orange), extensively drug resistant; PDR (red), pan drug resistant. *S: Serine carbapenemase; M*: Metallo-β-lactamase.