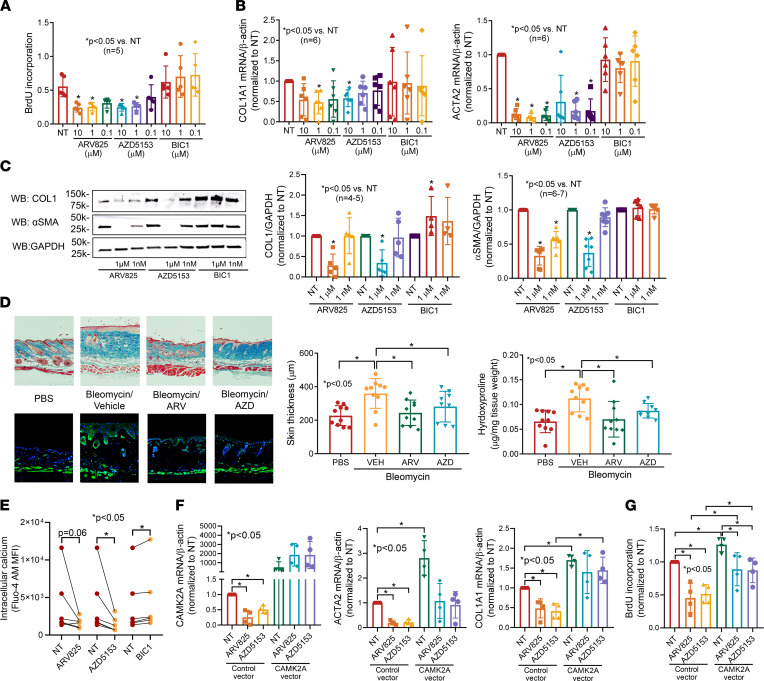
Figure 7. BRD4 inhibitors show prominent antifibrotic effects in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Treating dcSSc fibroblasts with the specific BRD2 inhibitor BIC1 had minimal effect on cell proliferation, whereas inhibition of BRD4 using BRD4 inhibitors AZD5153 or ARV825 significantly reduced cell proliferation at concentrations of 1 and 10 μM. n = 5 patients. (B) Inhibition of BRD4 by ARV825 or AZD5153 in dcSSc fibroblasts significantly reduced both ACTA2 and COL1A1 expression, whereas blockade of BRD2 by BIC1 had no effect. n = 6 patients. (C) BRD4 inhibitors significantly decreased α-SMA (n = 7) and COL1 (n = 5) in dcSSc fibroblasts, whereas BRD2 inhibition by BIC1 had minimal effect on α-SMA (n = 6) but increased COL1 at 1 μM (n = 4 patients). (D) Bleomycin-treated mice had increased dermal thickness and hydroxyproline content in skin, and ARV825 or AZD5153 efficiently prevented skin fibrosis in these mice. Immunofluorescence staining of α-SMA–positive cells (green) is shown. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Original magnification, ×40–100. n = 9–10 mice. (E) BRD4 inhibitor AZD5153 significantly decreased intracellular Ca2+ and BRD2 inhibitor BIC1 significantly increased it. n = 6 patients. (F) Overexpression of CAMK2A resulted in significant increase in ACTA2 and COL1A1 expression and blocked the effect of AZD5153 on COL1A1 expression. n = 4 patients. (G) CAMK2A overexpression significantly increased cell proliferation while it abolished the effect of BRD4 inhibition on cell proliferation. n = 4 patients. Results are expressed as mean ± SD and P < 0.05 was considered significant. Significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA (A–D, F, and G), Kruskal-Wallis test (A–C), and Wilcoxon’s test (E). NT, no treatment.