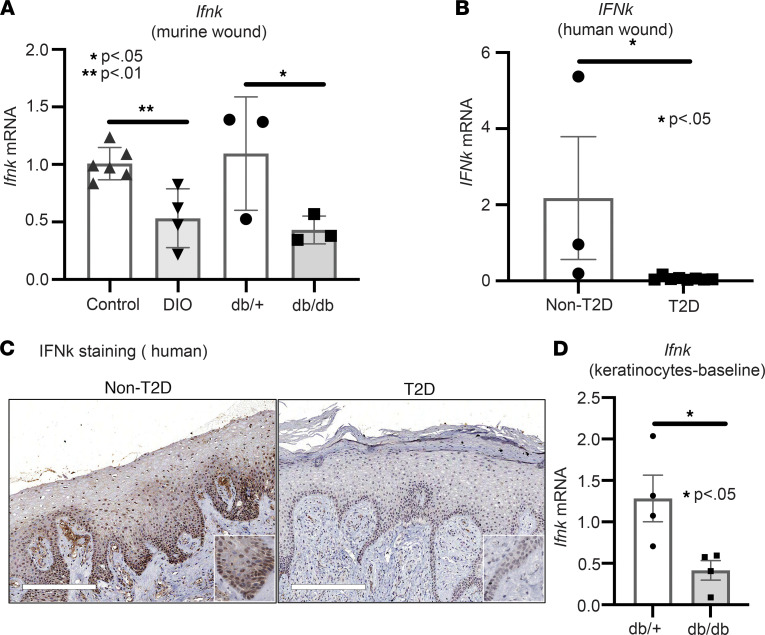
Figure 3. Impaired IFN-κ production in human diabetic wounds.
(A) Whole wounds were isolated from 2 diabetic models (DIO and db/db) and their respective controls; n = 3–6 per group. Ifnk gene expression was measured via qPCR. (B) Human wounds were collected from T2D patients with chronic diabetic foot ulcers and non-T2D; n = 3–8 per group. IFNk gene expression was measured via qPCR. (C) Representative staining for IFN-κ performed on wounds from T2D and non-T2D patient skin. Magnification, ×10. (D) Keratinocytes were isolated at baseline from the tail of db/db mice and their controls; n = 4 per group, repeated in triplicate. Ifnk expression was measured via qPCR. Data were analyzed for variances, and 2-tailed Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney U test was performed. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.