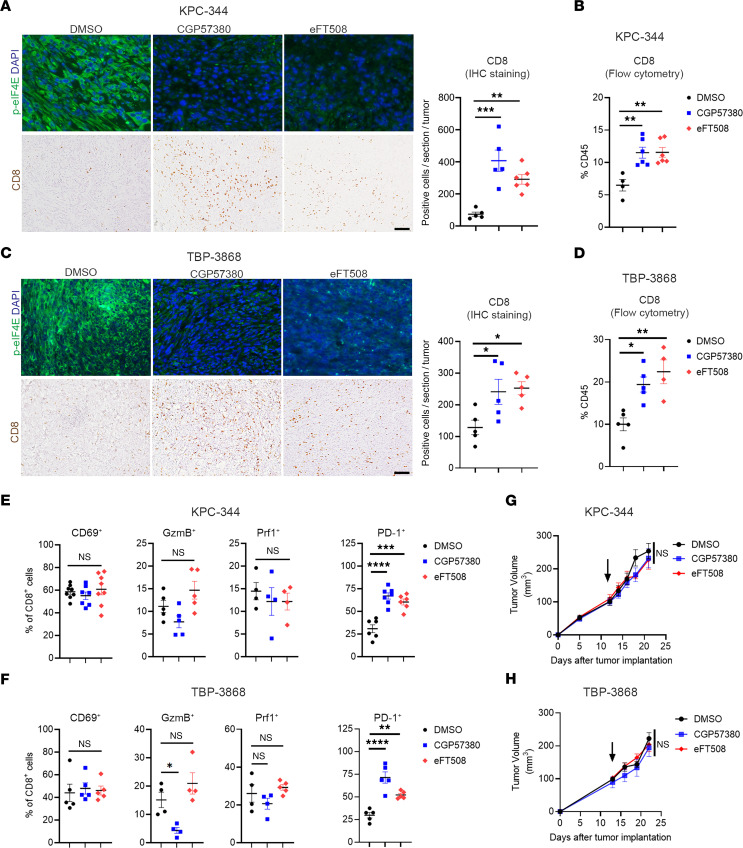
Figure 2. MNK inhibitors increase CD8+ T cells in tumors but induce a T cell exhaustive phenotype.
Mice with established syngeneic pancreatic (KPC-344) and thyroid (TBP-3868) tumors were randomized and treated with DMSO (vehicle control), the MNK inhibitor CGP57380 (25 mg/kg), or the MNK inhibitor eFT508 (1 mg/kg) daily. (A and C) The collected tumors were analyzed for p-eIF4E expression by immunofluorescence staining and CD8+ T cells by IHC staining. Scale bar: 100 μm. The absolute number of stained CD8+ T cells per 10× section was quantified by ImageJ and averaged from 5 individual sections. (B and D) The collected tumors were digested and analyzed by flow cytometry for the number of CD8+ T cells. (E and F) Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for the expression of CD69, granzyme B (GzmB), perforin-1 (Prf1), and PD-1. Data points in B, D, E, and F represent individual tumors. (G and H) Tumor size was monitored and measured using calipers. Tumor volumes (V) were calculated using the formula V = (W2 × L)/2, where W is tumor width and L is tumor length. Arrows indicate start of treatment. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM, and analysis was done using 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.