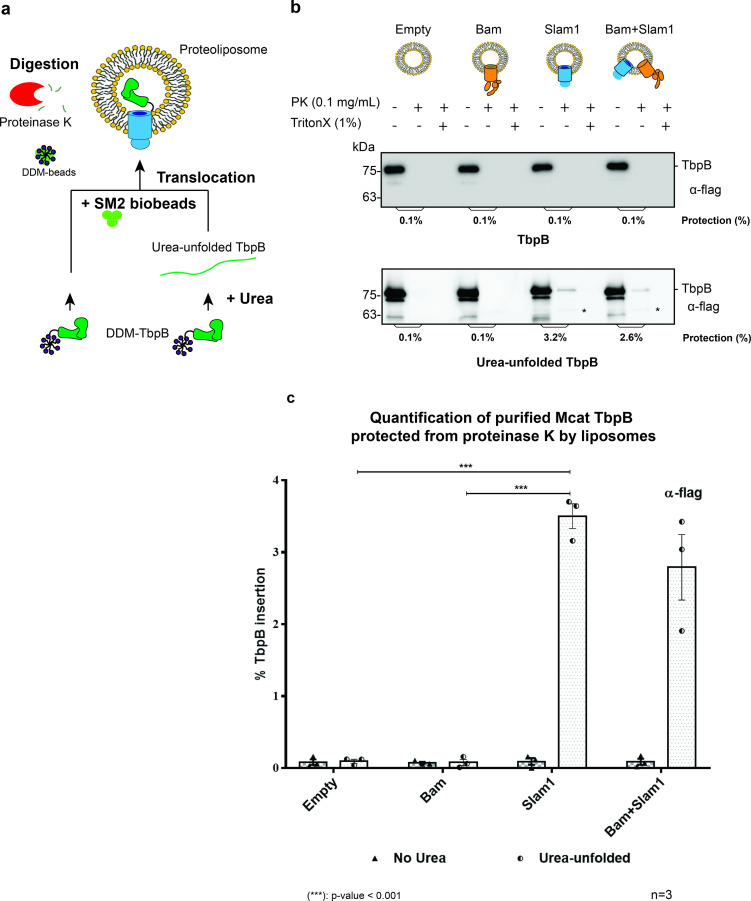
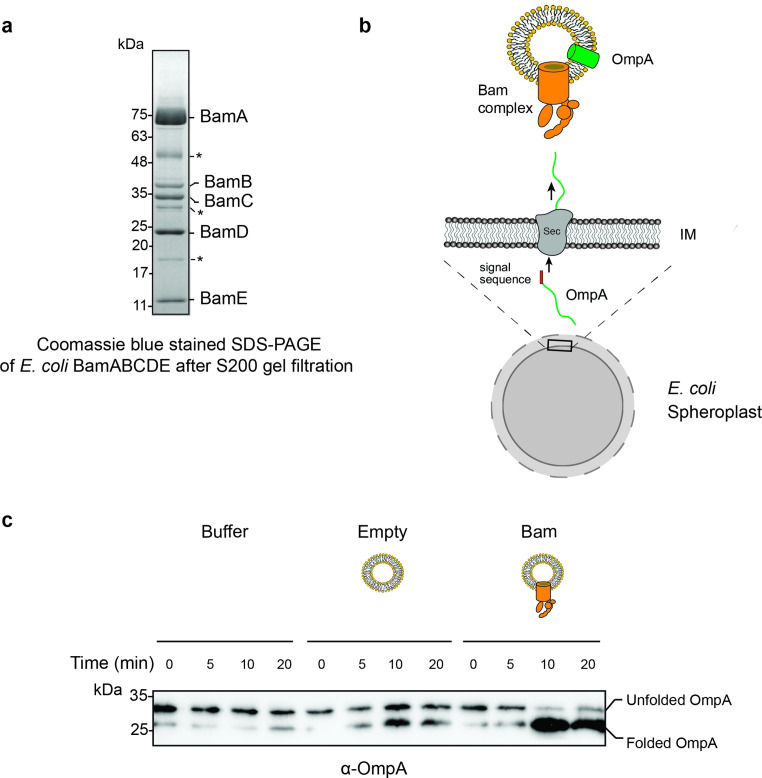
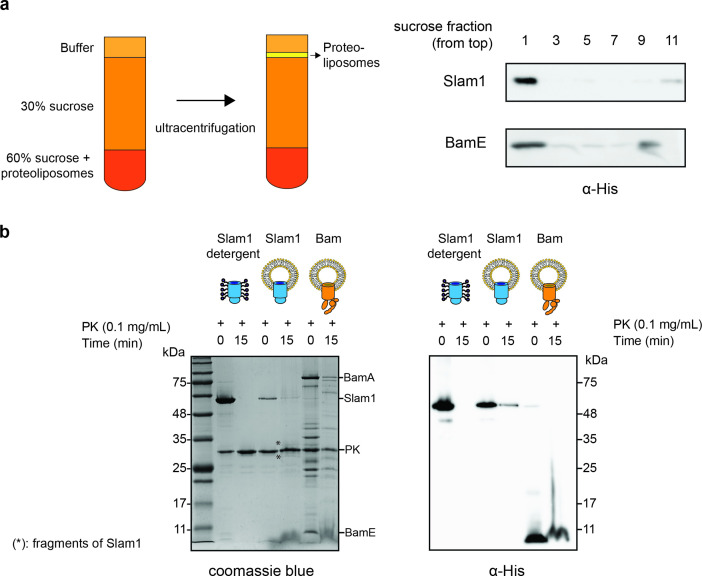
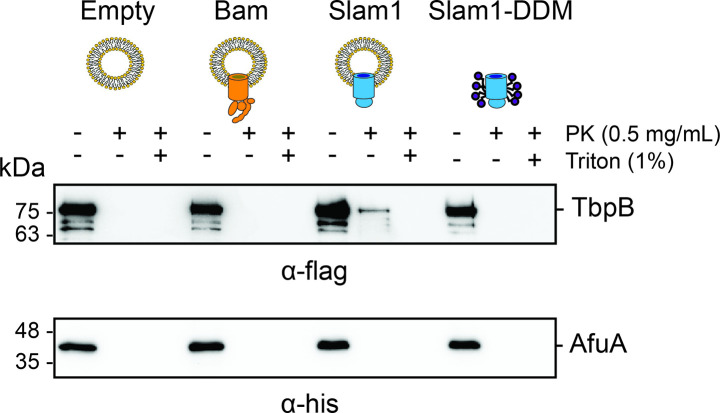
Figure 1. Slam1 is necessary for translocation of unfolded TbpB.
(a) Model of a defined in vitro assay for TbpB translocation. M. catarrhalis TbpB (folded and urea-unfolded) is translocated inside Slam1-containing proteoliposomes. SM2 biobeads were used to remove DDM detergent from TbpB before adding proteoliposomes for translocation. Efficiency of TbpB translocation/insertion was calculated based on percentage of TbpB that was protected from proteinase K. (b) Representative proteinase K protection assay results obtained for Slam1 or Slam1 + Bam incubated with purified TbpB (folded or kept unfolded by 8 M urea). Proteoliposomes containing Empty or Bam were used as controls. Each sample was treated with PK or PK + Triton X-100 and examined by western blot. α-flag antibody western blots were used to quantify the amount of TbpB. Asterisk (*) The lower band in the (+PK and −Triton X) samples in Slam1 and Bam + Slam1 proteoliposomes treatment likely represents incompletely translocated TbpB that has been partially degraded by proteinase K. (c) Quantification of TbpB protection in proteoliposomes through densitometry analysis. The % TbpB insertion was calculated by dividing the protected TbpB of + PK sample by TbpB of the input sample. The plot contains results obtained from three biological replicates. Individual data points were included on the graph. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was performed to determine the statistical significance for the translocation of unfolded TbpB by Slam1 proteoliposomes and Slam1 + Bam proteoliposomes treatment versus by the negative controls (empty liposomes and Bam proteoliposomes). Only statistical significance of the unfolded TbpB translocation by Slam1 proteoliposomes against the two negative controls are included on the blot for simplification. (***) represents p-value < 0.001.