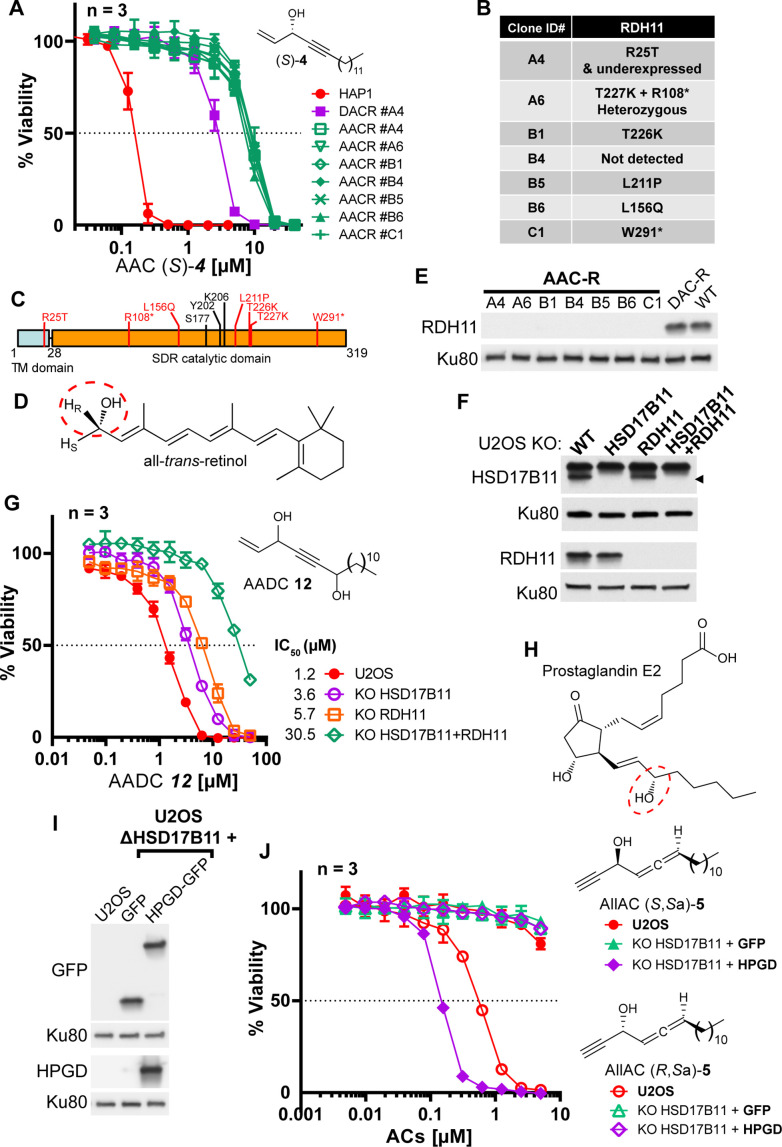
Figure 5. Bioactivation of other lipidic alkynylcarbinols by specific SDRs.
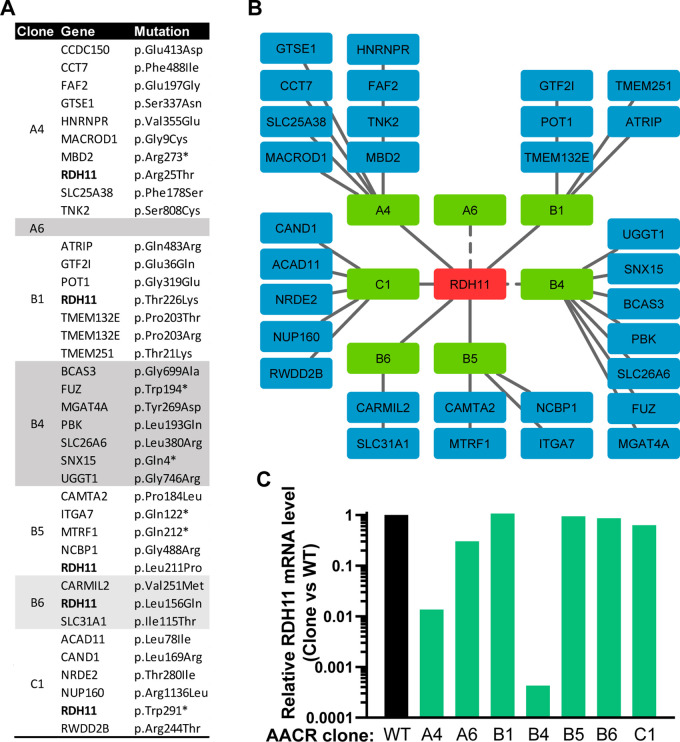
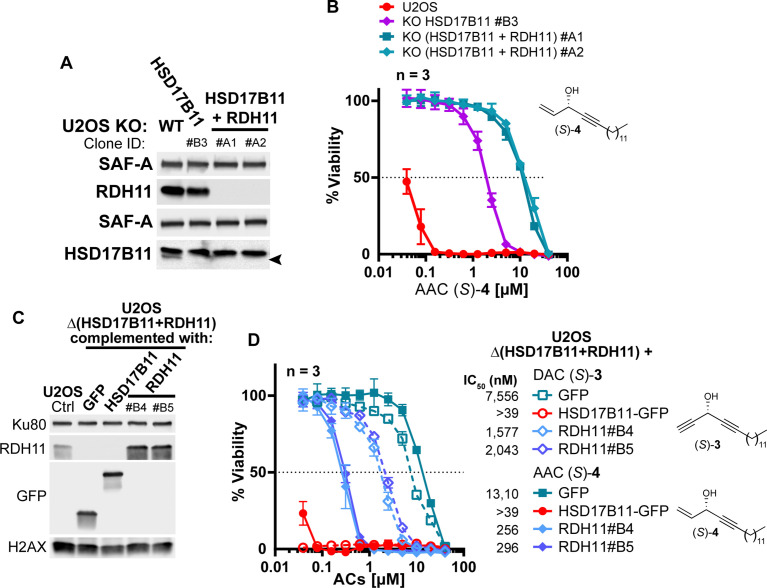
(A) Cell viability analysis of wild-type HAP-1, DACR clone A4 and AACR clones treated with AAC (S)–4. (B) List of mutations identified on RDH11 by RNA-seq of individual AACR clones. (C) Schematic representation of RDH11 with, in red, the positions of the mutations identified and, in black, the three amino acids critical for catalysis. TM = single-pass transmembrane domain. (D) Structure of all-trans-retinol, a substrate for RDH11. (E) Analysis by immunoblotting of RDH11 levels in wild-type HAP-1, in DACR clone A4 and in the different AACR clones. (F) Analysis by immunoblotting of RDH11 and HSD17B11 levels in wild-type U2OS or clones inactivated for either HSD17B11, RDH11 or both. (G) Cell viability analysis of wild-type U2OS or U2OS clones inactivated for HSD17B11, RDH11, or both and treated with AADC 12. (H) Structure of prostaglandin E2, a substrate of HPGD. (I) Analysis by immunoblotting of GFP and HPGD levels in WT U2OS or U2OS KO HSD17B11 stably complemented with GFP or HPGD-GFP. (J) Cell viability analysis of U2OS or U2OS inactivated for HSD17B11, stably complemented with either HSD17B11-GFP or HPGD-GFP and treated for 72 h with AllAC (S,Sa)- or (R,Sa)–5.