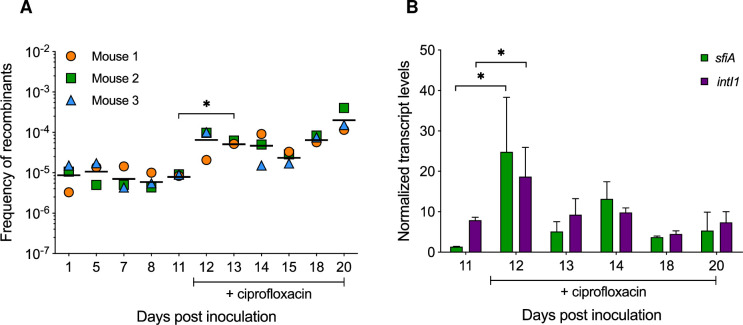
Fig 4. Effect of ciprofloxacin on the induction of the SOS response and the IntI1 integrase expression and activity in the mouse gut.
On day 0, three germ-free mice were inoculated with 108 CFU of MG/intI1 (carrying p6851 and pZE1intI1 allowing the expression of intI1 SOS-regulated). Ciprofloxacin was added to the drinking water of mice on day 11 post inoculation, just after the fecal sampling on that day. (A) Recombination activity of IntI1, reflected by the frequency of recombinants (FR), was estimated by determining the frequency of emergence of tobramycin-resistant recombinants, as a result of specific recombination between attC sites located on a synthetic array of two cassettes (attCaadA7-cat(T4)-attCVCR2-aac(6’)-Ib*) carried on plasmid p6851. Each symbol represents the FR in the gut calculated from a single mouse exhibiting recombinants. For each sampling day, the average FR is shown as a black horizontal line. (B) Transcript levels of sfiA and intI1 genes in the mouse gut are represented. Transcript levels were normalized to the housekeeping gene dxs. Error bars indicate the SD. Differences were determined using the Mann-Whitney U test. *p < 0.05.