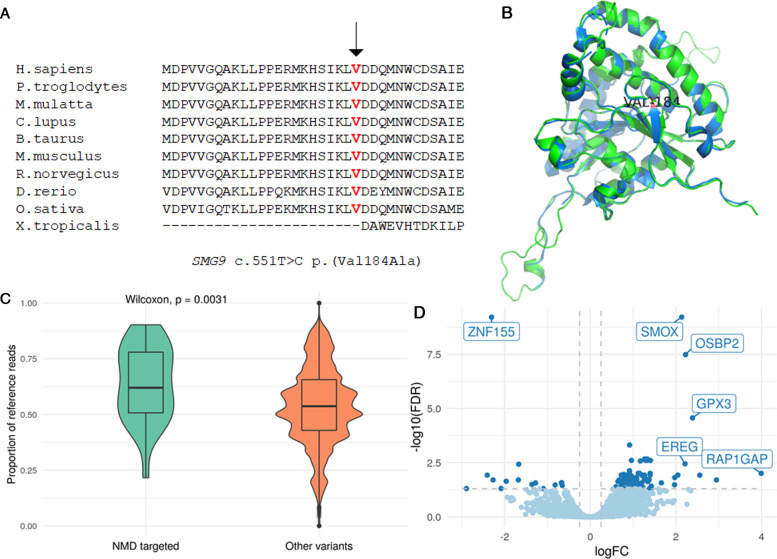
Fig. 3. Evidence for the effect of SMG9 c.551T > C p.(Val184Ala) variant.
A Multispecies alignment showing the strong conservation of SMG9 p.Val184 B The predicted SMG9-Val184Ala mutated structure (green) superimposed on the wild-type SMG9 structure (blue) showing a predicted structural alteration. C Plot comparing the proportion of reference reads from allele-specific expression analysis in likely NMD-targeted variants (n = 20) compared to non-protein-truncating variants (n = 27,046) in Patients 1–4. The proportion of reference reads was significantly higher in predicted NMD-targeted variants than other variants, suggesting a functional PTC-induced NMD system in patients. D Volcano plot showing DEGs between the patients and healthy controls. The overall pattern observed was the increased expression of genes in the patient group compared with the control group. The dark blue dots show statistically significant DEGs (FDR padj < 0.05 and |logFC| > = 0.25). The boxes show the genes that display both large magnitude fold-changes (FC) and high statistical significance (FDR padj).