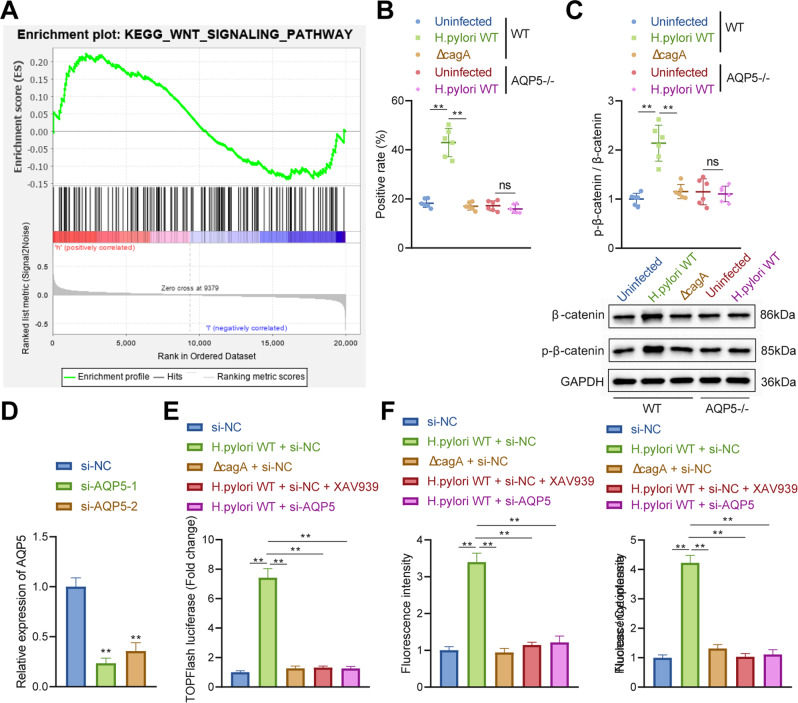
Fig. 5. H. pylori infection facilitates the activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway by upregulating AQP5.
A The differences in enriched pathways between AQP5 high expression and low expression groups analyzed by GSEA. B β-catenin expression in gastric mucosa of mice detected by immunohistochemistry (n = 6). C β-catenin protein level in gastric mucosa of mice detected by Western blot analysis (n = 6). D AQP5 mRNA level in AGS cells determined by RT-qPCR. E The activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in primary GECs of mice detected by TOPFlash luciferase reporter assay. F β-catenin expression in mouse primary GECs detected by immunofluorescence staining. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns not significant. Data were shown as the mean ± standard deviation. Cell experiments were repeated three times independently. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test was applied for the comparison of data among multiple groups.