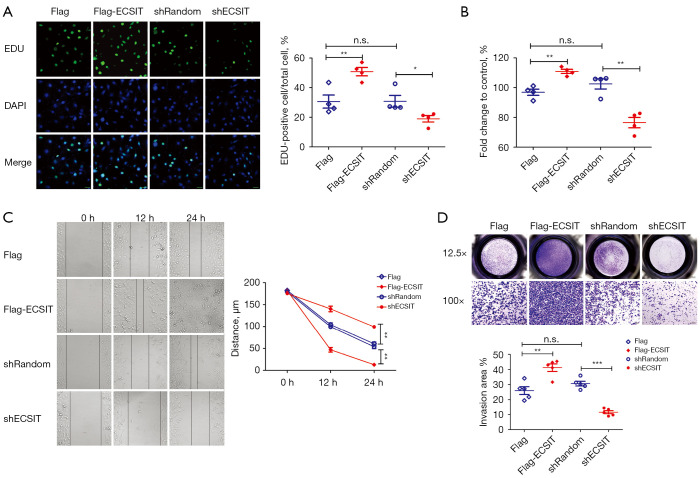
Figure 1.
Effects of ECSIT on biological functions in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. (A) Immunofluorescence of EUD-positive MDA-MB-231 cells. Representative images (scale bar =30 µm) and quantification of EDU-positive cells are shown (right panel; n=4). (B) Relative cell viability of MDA-MB-231 cells was detected by a CCK-8 (n=4). (C) Cell migration capacities were evaluated by a wound-healing assay. Representative microscopic images are shown in the left panels. The wound-healing distance (µm) was calculated with ImageJ software (right panel; n=5). (D) Representative microscopic images are shown in the upper panels. Cell invasion capacities were evaluated by comparing the numbers of invaded cells (lower panel; n=5). Statistical significance was calculated for the indicated paired samples with *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01 and ***, P<0.001; n.s., no significance. Cells were transiently transfected with Flag or Flag-ECSIT plasmid, and stable cell lines were generated with shRandom or shECSIT. EDU, 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine; DAPI, 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; CCK-8, cell counting Kit-8; ECSIT, evolutionarily conserved signaling intermediate in Toll pathways.