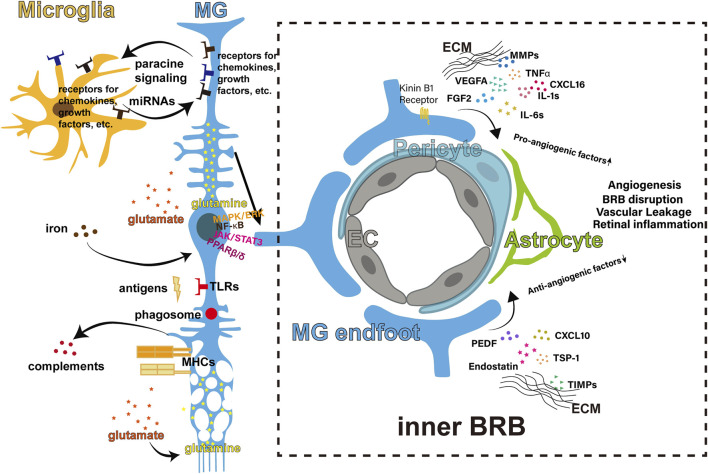
FIGURE 1.
Regulations of retinal inflammation from the MG. The body of the MG spans across the retina. The MG interact with the microglia in the inner retina through cytokines paracrine signaling and miRNAs. The main signaling pathways involved include MAPK/ERK, NF-κB, JAK/STAT3 and PPARβ/δ. The MG intake the glutamate released by neurons and convert the neurotoxic glutamate to non-toxic glutamine. The MG take in excessive iron and prevent iron-induced inflammation. The MG express TLRs and recognize antigens after infection, and are capable of phagosome-dependent clearance. The MG can express MHCs and release complements. The endfoot of the MG is crucial part of the inner BRB, regulating angiostasis through pro- and anti-angiogenic factors. BRB, blood-retinal barrier; EC, endothelial cells; EMC, extracellular matrix; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MG, Müller glia; miRNA, micro-RNA.