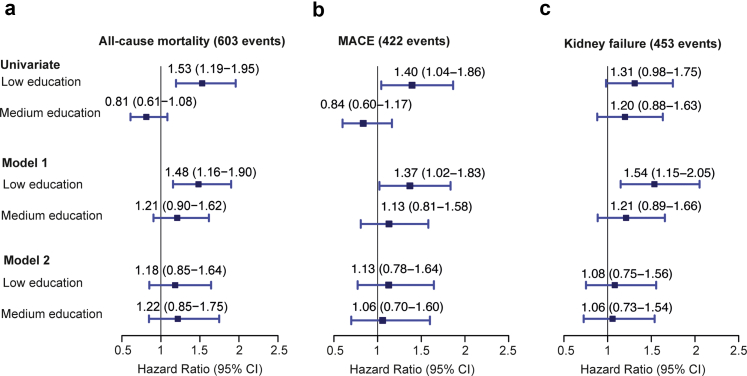
Figure 2.
Association of educational attainment with all-cause mortality, MACE, and kidney failure in GCKD cohort study participants included in the current analyses. Results are presented as HRs with 95% CIs given in parentheses. The size of the square representing a relative risk is proportional to its inverse variance. High educational attainment served as the reference group. Model 1: Cox proportional hazard model adjusted for age and gender. Model 2: Cox proportional hazard model adjusted for age, gender, eGFR, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio, and all potential mediators identified by mixed graphical model including BMI, smoking status (former + current vs. never smoker), alcohol consumption (≥3×/wk vs. <3×/wk), cardiovascular disease (yes vs. no), systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medication (yes vs. no), HDL cholesterol, triglycerides, uric acid, calcium, urea, sodium, serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, bone-specific alkaline phosphatase, C-reactive protein, intact plasma parathyroid hormone, N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide, high-sensitive troponin T, OPN, H-FABP, income (<25,000€ vs. ≥25,000€), and health insurance (private vs. public). BMI, body mass index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; GCKD, German Chronic Kidney Disease; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HR, hazard ratio; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; UACR, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio.