Table 3.
Logistical regression for the outcome nonstandard dialysis start
| Odds ratio | 95% CI |
P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Higher | ||||
| CCI (≥8) | 0.863 | 0.344 | 2.150 | 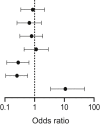 |
0.752 |
| BMI (≥30 kg/m2) | 0.662 | 0.254 | 1.689 | 0.389 | |
| Gender (male) | 0.788 | 0.318 | 1.888 | 0.597 | |
| Diabetes, NAS vs. others | 1.129 | 0.442 | 2.895 | 0.799 | |
| eGFR (<7 ml/min per 1.72 m2) | 0.279 | 0.115 | 0.646 | 0.004 | |
| Urgent vs. planned start | 0.254 | 0.106 | 0.581 | 0.002 | |
| Intensive predialysis vs. conventional care | 10.826 | 3.452 | 48.220 | <0.001 | |
BMI, body mass index; CCI, Charlson comorbidity index; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate according to the CKD-Epidemiology Collaboration formula; NAS, nephroangiosclerosis.
The Pearson phi coefficient64 was equal to 0.271 between urgent start and intensive predialysis care origin (both were kept in the model) and 0.57 between age and CCI, thus only the Charlson score was used.
Bold value indicates significant differences.
