Figure 1.
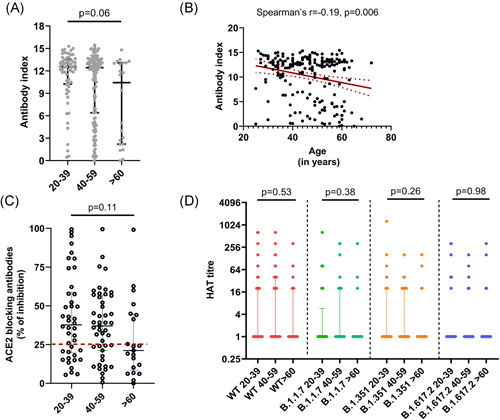
SARS‐CoV‐2 specific antibody responses 3 months following the second dose (16 weeks following the first dose) of the Sinopharm/BBIBP‐CorV vaccine. SARS‐CoV‐2 specific total antibodies were measured in 20–39 years old (n = 61), 40–59 years old (n = 120) and those ≥60 years of age (n = 22) by ELISA and no significant difference was seen between the age groups (p = .06) based on the Kruskal–Wallis test (A). The total antibody titres inversely correlated (Spearman's r = −.19, p = .006) with age (B) (the red dotted lines indicate the 95% confidence interval). The ACE2 receptor blocking antibodies were measured by the surrogate virus neutralizing test in 20–39 years old (n = 41), 40–59 years old (n = 48) and ≥60 years old (n = 21) and no significant difference was seen (p = .11) between the age groups based on the Kruskal–Wallis test (C). Antibodies were measured to the receptor‐binding domain of the ancestral SARS‐CoV‐2 virus (WT) and to B.1.1.7, B.1.351 and B.1.617.2 using the haemagglutination test (HAT) in 20–39 years old (n = 41), 40–59 years old (n = 48) and ≥60 years old (n = 21) and no significant difference was seen (p = .11) between the age groups based on the Kruskal–Wallis test for different variants (D). All tests were two‐tailed. The lines indicate the median and the interquartile range. ELISA, enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay
