FIGURE 3.
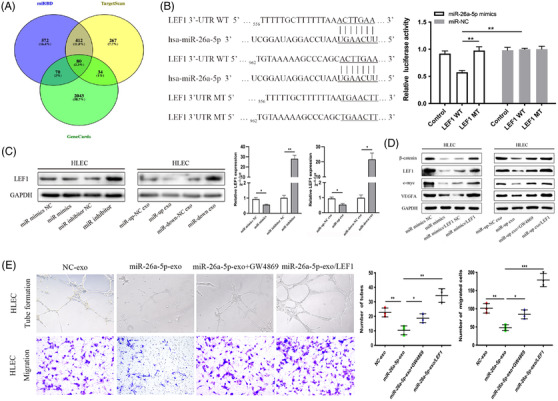
EC‐secreted exosomal miR‐26a‐5p targets LEF1 induced lymphatic vessel formation in HLECs. (A) miR‐26a‐5p target predictions identified from different databases (miRDB, TargetScan and GeneCards). (B) Sequence alignment between miR‐26a‐5p and the 3′‐UTR of LEF1 (left), and effects of miR‐26a‐5p mimics/NC on the luciferase reporter activity in wild type (WT) and mutant type (MT) (right). (C) Protein and mRNA levels of LEF1 assessed through western blotting and qRT‐PCR, respectively, in HLECs, after transfection with miR‐26a‐5p mimics/inhibitor or indicated exosomes. (D) β‐catenin, LEF1, c‐myc and VEGFA protein levels were detected by western blotting in HLECs treated with an miR‐26a‐5p mimics, indicated exosomes from GW4869‐pre‐treated EC cells, or in the presence of LEF1 overexpression plasmid. (E) Upregulation of LEF1 reversed the biological effects of exosomal miR‐26a‐5p, as evaluated by tube formation and cell migration experiments. Mean ± SD are provided (n = 3). *p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001
