FIG. 1.
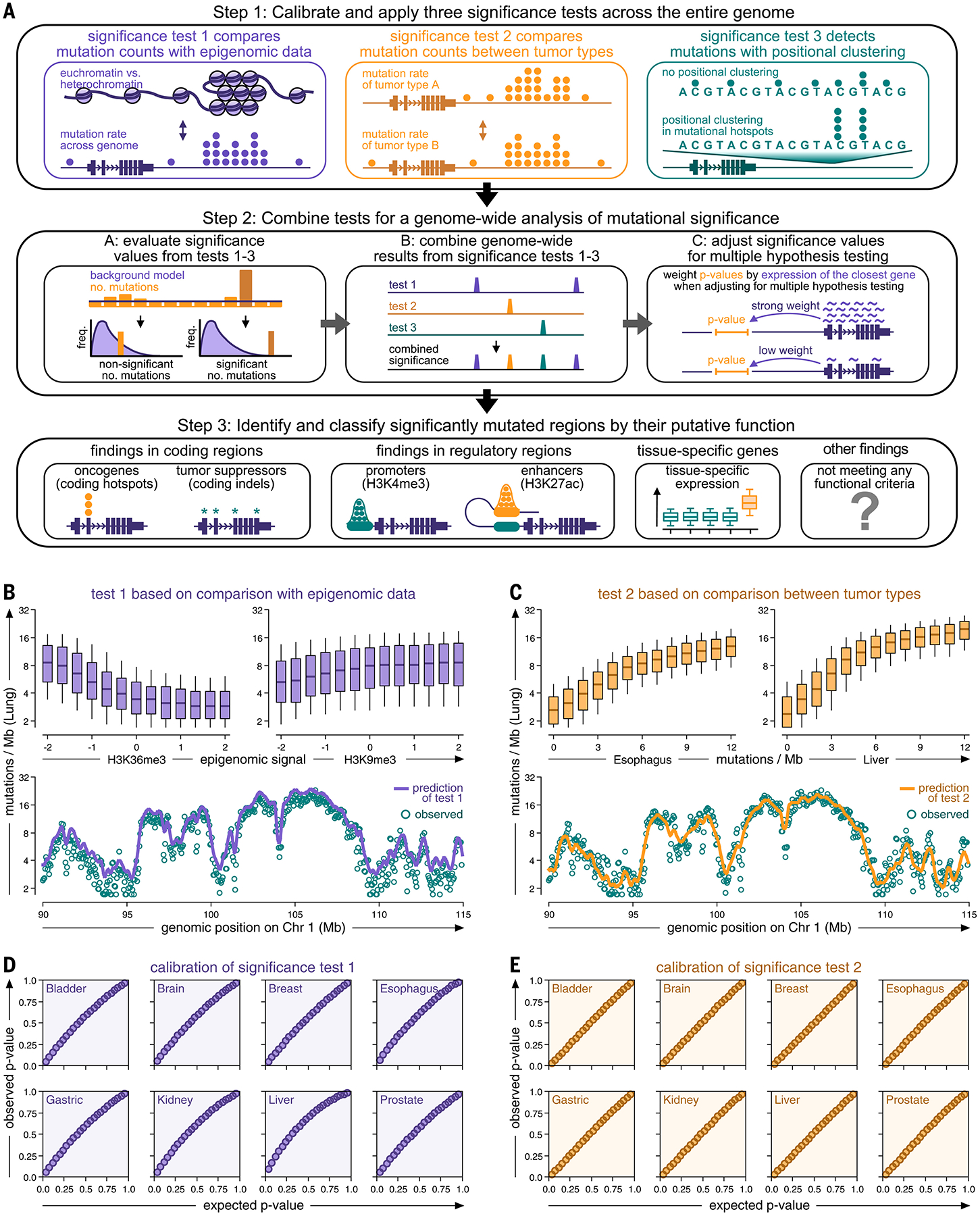
Genome-wide analysis of somatic mutation events in whole cancer genomes. (A) Genome-wide detection of somatic mutation events in whole cancer genome sequencing data. Step 1 combines three complementary test strategies. Step 2 integrates the results of tests 1 to 3 into a joint, genome-wide signal and identifies significant mutation events. Step 3 classifies mutation events according to their genomic location. (B and C) Top: Boxplots comparing mutation rates of a representative cancer type (lung cancer) against epigenomic signals [(B), the rationale of test 1] and mutation rates of other cancer types [(C), the rationale of test 2]. Boxes indicate 25/75% interquartile ranges, vertical lines extend to 10/90% percentiles, and horizontal lines reflect distribution medians. Bottom: Observed (teal dots) and predicted (continuous line) mutation rates (10-kb intervals) plotted against their position on chromosome 1 (function smoothed by Gaussian kernel). (D and E) Q-Q plots comparing observed (y-axis) and expected (x-axis) P values for test 1 (D) and test 2 (E).
